Role of Homeobox A1 in Airway Epithelial Generation from Human Airway Basal Cells
- PMID: 40214503
- PMCID: PMC11989199
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14070549
Role of Homeobox A1 in Airway Epithelial Generation from Human Airway Basal Cells
Abstract
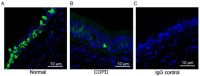
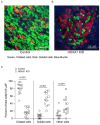
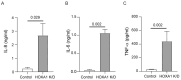
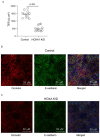
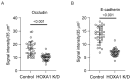
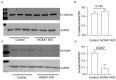
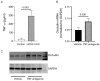
Airway basal cells from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients show a reduction in HOXA1 expression and generate an abnormal airway epithelium. Because the specific role of HOXA1 in airway basal cells is not known, we investigated the contribution of HOXA1 in the generation of the airway epithelium, which depends on basal cell proliferation, polarization, and differentiation. Airway stem cells were transduced with an inducible HOXA1 shRNA lentivector to knock down HOXA1 in either proliferating cells or100% confluent cells. The bronchial epithelium expresses HOXA1 near the basement membrane, likely representing basal cells. HOXA1 knockdown in proliferating basal cells attenuated cell proliferation. HOXA1 knockdown in confluent monolayers of basal cells generated an abnormal airway epithelium characterized by goblet cell hyperplasia and an inflammatory phenotype. Compared to the control, HOXA1 knockdown cells showed a decrease in transepithelial resistance, localization of occludin and E-cadherin to the intercellular junctions, reduced expression of occludin but not E-cadherin, and increased expression of TNF-α. Blocking TNF-α increased the expression of occludin in HOXA1 K/D cells. Based on these results, we conclude that HOXA1 plays an important role in cell proliferation, polarization, and differentiation, which are essential steps in airway epithelial generation. Additionally, HOXA1 may regulate occludin expression by inhibiting TNF-α expression.
Keywords: airway epithelial repair; cell polarization; cell proliferation; goblet cell metaplasia; mucociliary-differentiated cell cultures; occludin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HOXA1 Contributes to Bronchial Epithelial Cell Cycle Progression by Regulating p21/CDKN1A.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 5;26(5):2332. doi: 10.3390/ijms26052332. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076953 Free PMC article.
-
{alpha}7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor regulates airway epithelium differentiation by controlling basal cell proliferation.Am J Pathol. 2009 Nov;175(5):1868-82. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.090212. Epub 2009 Oct 1. Am J Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19808646 Free PMC article.
-
HOXA1 is required for E-cadherin-dependent anchorage-independent survival of human mammary carcinoma cells.J Biol Chem. 2006 Mar 10;281(10):6471-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M512666200. Epub 2005 Dec 22. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16373333
-
Elevated HOXA1 expression correlates with accelerated tumor cell proliferation and poor prognosis in gastric cancer partly via cyclin D1.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Jan 21;35:15. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0294-2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26791264 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase D promotes airway epithelial barrier dysfunction and permeability through down-regulation of claudin-1.J Biol Chem. 2013 Dec 27;288(52):37343-54. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.511527. Epub 2013 Nov 21. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24265314 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rock J.R., Hogan B.L. Epithelial progenitor cells in lung development, maintenance, repair, and disease. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011;27:493–512. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

