Towards MRI Study of Biointegration of Carbon-Carbon Composites with Ca-P Coatings
- PMID: 40214538
- PMCID: PMC11990118
- DOI: 10.3390/nano15070492
Towards MRI Study of Biointegration of Carbon-Carbon Composites with Ca-P Coatings
Abstract
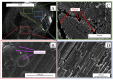
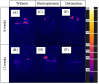
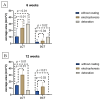
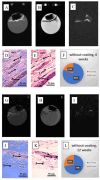
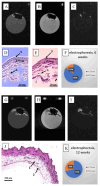
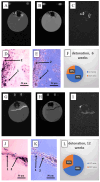
The development of specific MRI criteria to monitor the implantation process may provide valuable information of individual tissue response. Using MRI and histological methods, the biointegration of carbon-carbon (C-C) composites into the subcutaneous tissues of BDF1 mice and their biocompatibility were investigated. The study focused on autopsy specimens containing C-C composite implants, both uncoated and coated with synthetic hydroxyapatite (Ca-P) via electrodeposition or detonation techniques, assessed at 6 and 12 weeks post-implantation. The results revealed that the radiological characteristics of the connective tissue capsule surrounding the implants allowed for the differentiation between loose and dense connective tissues. Fat-suppressed T1-weighted MRI scans showed that the volume of both loose and dense connective tissue in the capsule increased proportionally at 6 and 12 weeks, with distinct ratios observed between the coated and uncoated specimens. The proposed MRI criteria provided a strategy for evaluating the density and homogeneity of the connective tissue capsule. This approach could be valuable for further non-invasive in vivo studies on implant biointegration.
Keywords: MRI; carbon-carbon medical composites; detonation spraying; electrophoretic deposition; fibrous capsule; hydroxyapatite coatings; radiology studies; tissue response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Electrophoretic Deposition of Calcium Phosphates on Carbon-Carbon Composite Implants: Morphology, Phase/Chemical Composition and Biological Reactions.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 16;25(6):3375. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063375. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542348 Free PMC article.
-
Surface modification of corneal prosthesis with nano-hydroxyapatite to enhance in vivo biointegration.Acta Biomater. 2020 Apr 15;107:299-312. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.01.023. Epub 2020 Jan 22. Acta Biomater. 2020. PMID: 31978623
-
A novel suprachoroidal microinvasive glaucoma implant: in vivo biocompatibility and biointegration.BMC Biomed Eng. 2020 Oct 14;2:10. doi: 10.1186/s42490-020-00045-1. eCollection 2020. BMC Biomed Eng. 2020. PMID: 33073174 Free PMC article.
-
Ion-substituted calcium phosphate coatings by physical vapor deposition magnetron sputtering for biomedical applications: A review.Acta Biomater. 2019 Apr 15;89:14-32. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.03.006. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Acta Biomater. 2019. PMID: 30851454 Review.
-
Electrophoretic Deposition of Biocompatible and Bioactive Hydroxyapatite-Based Coatings on Titanium.Materials (Basel). 2021 Sep 18;14(18):5391. doi: 10.3390/ma14185391. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34576615 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Narayan R. Biomedical Materials. 3rd ed. Springer Science + Business Media; New York, NY, USA: 2009. pp. 123–154.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

