Research on Flexible Sensors for Wearable Devices: A Review
- PMID: 40214565
- PMCID: PMC11990515
- DOI: 10.3390/nano15070520
Research on Flexible Sensors for Wearable Devices: A Review
Abstract
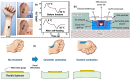
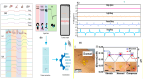
With the development of new materials and the trend of miniaturization of smart devices, wearable devices are playing an increasingly important role in people's lives and occupying a larger market share. Meanwhile, the operation of wearable devices is based on the flexible sensors inside them. Although the development of flexible sensors has been very rapid in the more than 20 years since entering the 21st century, facing the booming market and demand at present, the development of flexible sensors still faces many challenges such as more miniaturization, higher integration, greater sustainability, high precision, and more efficient energy saving. This paper aims to summarize the development of flexible sensors, look forward to the future development of such devices, and provide a reference for researchers.
Keywords: biosignal; flexible sensors; longtime monitoring; real-time feedback; smart devices; wearable devices.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Exploration on flexible wearable sensor motion monitoring based on novel functional polymer conjugated materials.Front Chem. 2023 Dec 1;11:1265211. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1265211. eCollection 2023. Front Chem. 2023. PMID: 38107253 Free PMC article.
-
Revolutionizing human healthcare with wearable sensors for monitoring human strain.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2025 Feb;246:114384. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2024.114384. Epub 2024 Nov 17. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2025. PMID: 39579495 Review.
-
Flexible wearable sensors for crop monitoring: a review.Front Plant Sci. 2024 May 29;15:1406074. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1406074. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38867881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Progress of Research into Flexible Sensors in the Field of Smart Wearables.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jul 6;22(14):5089. doi: 10.3390/s22145089. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35890768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Flexible Wearable Technology: From Textile Fibers to Devices.Chem Rec. 2024 Mar;24(3):e202300361. doi: 10.1002/tcr.202300361. Epub 2024 Feb 16. Chem Rec. 2024. PMID: 38362667 Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

