Renoprotective effects of combination therapy with tolvaptan and dapagliflozin in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: a four-case series
- PMID: 40214869
- PMCID: PMC12126371
- DOI: 10.1007/s13730-025-00990-7
Renoprotective effects of combination therapy with tolvaptan and dapagliflozin in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: a four-case series
Abstract
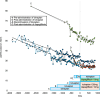
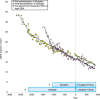
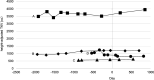
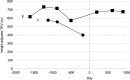
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), the most prevalent inherited kidney disorder, progresses inexorably to end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) with the vasopressin V2-receptor antagonist tolvaptan serving as a primary treatment option since 2014. While dapagliflozin, a sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, was approved for treating chronic kidney disease in August 2021, its renoprotective effects in ADPKD remain uncertain due to potential vasopressin stimulation. We evaluated four Japanese ADPKD patients receiving combination therapy with tolvaptan and dapagliflozin for over two years. A 74-year-old woman (Mayo Class 1D, CKD stage 4) showed improved estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) decline from - 1.39 to - 0.66 mL/min/1.73 m2/year. A 62-year-old woman (Mayo Class 1B, CKD stage 3b) demonstrated eGFR decline improvement from - 1.02 to - 0.66 mL/min/1.73 m2/year. A 39-year-old man (Mayo Class 1C, CKD stage 3a) exhibited significant improvement from - 5.00 to - 1.35 mL/min/1.73 m2/year. A 45-year-old woman (Mayo Class 1D, CKD stage 3b) showed marked improvement from - 14.12 to - 0.22 mL/min/1.73 m2/year. While eGFR decline decelerated in the control group, the combination therapy group showed more pronounced improvements. Height-adjusted total kidney volume (htTKV) in the group combination therapy showed variable responses: two patients experienced volume increases (+ 4.03%, + 3.65%/year), while two showed decreases (- 0.45%, - 3.65%/year). These cases suggest potential renoprotective benefits from combining tolvaptan and dapagliflozin in ADPKD patients. Careful monitoring of renal cyst enlargement is warranted with concurrent dapagliflozin use. Further research is needed to confirm these preliminary findings and establish optimal patient selection criteria for combination therapy.
Keywords: Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease; Estimated glomerular filtration rate decline; Height-adjusted total kidney volume; Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor; Vasopressin V2-Receptor antagonist.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: A Review.JAMA. 2025 May 20;333(19):1708-1719. doi: 10.1001/jama.2025.0310. JAMA. 2025. PMID: 40126492 Review.
-
Additional renoprotective effect of the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin in a patient with ADPKD receiving tolvaptan treatment.CEN Case Rep. 2024 Oct;13(5):419-424. doi: 10.1007/s13730-024-00859-1. Epub 2024 Mar 18. CEN Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38494546 Free PMC article.
-
Tolvaptan in Japanese patients with later-stage autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.J Nephrol. 2018 Dec;31(6):961-966. doi: 10.1007/s40620-018-0545-8. Epub 2018 Oct 24. J Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 30357715
-
The safety and efficacy of tolvaptan in the treatment of patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Nefrologia (Engl Ed). 2023 Nov-Dec;43(6):731-741. doi: 10.1016/j.nefroe.2023.04.002. Epub 2023 May 5. Nefrologia (Engl Ed). 2023. PMID: 37150675
-
Prostaglandin E2, Osmoregulation, and Disease Progression in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2023 Nov 1;18(11):1426-1434. doi: 10.2215/CJN.0000000000000269. Epub 2023 Aug 14. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37574650 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Higashihara E, et al. Prevalence and renal prognosis of diagnosed autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease in Japan. Nephron. 1998;80(4):421–7. 10.1159/000045214. (PMID: 9832641). - PubMed
-
- Hanafusa N, et al. on behalf of Japanese Society for Dialysis Therapy Renal Data Registry Committee. 2022 Annual Dialysis Data Report, JSDT Renal Data Registry. (in Japanese). Journal of Japanese Society for Dialysis Therapy 2022;56(12):473–536.
-
- Heerspink HJL, et al.; DAPA-CKD Trial Committees and Investigators. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N Engl J Med. 2020 Oct 8;383(15):1436–1446. 10.1056/NEJMoa2024816. Epub 2020 Sep 24. PMID: 32970396. - PubMed
-
- EMPA-KIDNEY Collaborative Group; Herrington WG, et al. Empagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N Engl J Med 2022. 10.1056/ NEJMoa2204233
-
- Kei Fukamizu, et al. Japanese Society of Nephrology Recommendation on the correct use of SGLT2 inhibitors in the treatment of CKD. (in Japanese). The Japanese Journal of Nephrology 2023;65(1):1–10.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

