Efficacy and Safety of Tirzepatide Compared with GLP-1 RAs in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Treated with Basal Insulin: A Network Meta-analysis
- PMID: 40214900
- PMCID: PMC12085526
- DOI: 10.1007/s13300-025-01728-5
Efficacy and Safety of Tirzepatide Compared with GLP-1 RAs in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Treated with Basal Insulin: A Network Meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: The relative efficacy and safety of tirzepatide was compared with glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) treated with basal insulin using a network meta-analysis (NMA).
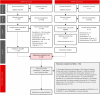
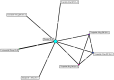
Methods: A systematic literature review was performed to identify randomized controlled trials of GLP-1 RAs in patients with T2DM treated with insulin and an antihyperglycaemic drug. For the NMA, studies included trials with 100% of patients treated with basal insulin background therapy with a titration scheme comparable to the SURPASS-5 trial. The following data were extracted for efficacy and safety assessment at the primary endpoint of each study: changes from baseline in glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) and body weight and the incidence of nausea, vomiting or diarrhoea, hypoglycaemia, and patients discontinuing treatment because of adverse events. In this study, a comparative analysis of tirzepatide was performed with the GLP-1 RAs dulaglutide, exenatide, and lixisenatide in addition to placebo.
Results: A total of six studies were included across the analyses. Tirzepatide 5, 10, and 15 mg showed statistically significant, greater reductions in HbA1c and body weight at the primary endpoint versus all GLP-1 RA comparators and placebo. Tirzepatide 5, 10, and 15 mg showed a statistically significant, higher likelihood of experiencing nausea compared with those who received placebo or exenatide 2 mg; no statistically significant differences were observed when compared with all other GLP-1 RA comparators. No statistically significant differences were observed in the proportions of patients who discontinued treatment because of adverse events when tirzepatide 5, 10, and 15 mg were compared with GLP-1 RA comparators, apart from tirzepatide 10 and 15 mg versus placebo.
Conclusion: Tirzepatide demonstrated statistically significantly greater reductions in HbA1c and body weight when compared with selected GLP-1 RAs and placebo in patients with T2DM treated with basal insulin. Overall, the safety profile of tirzepatide was similar to that of GLP-1RAs.
Keywords: Basal insulin; GLP-1 receptor agonists; Glycaemic control; Network meta-analysis; Tirzepatide; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of Interest: Beatrice Osumili, Kari Ranta, Hélène Sapin, and Jim S. Paik are employees and minor shareholders of Eli Lilly and Company. Zhengyu Yang was an employee and shareholder of Eli Lilly and Company during the development of the NMA and the manuscript and is currently an employee of Amylyx Pharmaceuticals. Matthias Blüher received honoraria as a consultant and speaker for Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eli Lilly and Company, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and Sanofi. Ethical Approval: This article is based on previously conducted studies and does not contain any new studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Once-Daily Oral Semaglutide Versus Injectable GLP-1 RAs in People with Type 2 Diabetes Inadequately Controlled on Basal Insulin: Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis.Diabetes Ther. 2021 May;12(5):1325-1339. doi: 10.1007/s13300-021-01034-w. Epub 2021 Mar 16. Diabetes Ther. 2021. PMID: 33723769 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis of head-to-head clinical trials comparing incretin-based glucose-lowering medications and basal insulin: An update including recently developed glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists and the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide/GLP-1 receptor co-agonist tirzepatide.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2023 May;25(5):1361-1371. doi: 10.1111/dom.14988. Epub 2023 Feb 8. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2023. PMID: 36700380
-
Tirzepatide, a dual GIP/GLP-1 receptor co-agonist for the treatment of type 2 diabetes with unmatched effectiveness regrading glycaemic control and body weight reduction.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022 Sep 1;21(1):169. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01604-7. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022. PMID: 36050763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Systematic Literature Review and Network Meta-Analysis Comparing Once-Weekly Semaglutide with Other GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Previously Receiving Basal Insulin.Diabetes Ther. 2018 Jun;9(3):1233-1251. doi: 10.1007/s13300-018-0428-y. Epub 2018 Apr 30. Diabetes Ther. 2018. PMID: 29713961 Free PMC article.
-
Tirzepatide: A Review in Type 2 Diabetes.Drugs. 2024 Feb;84(2):227-238. doi: 10.1007/s40265-023-01992-4. Epub 2024 Feb 23. Drugs. 2024. PMID: 38388874 Review.
References
-
- Landgraf R, Aberle J, Birkenfeld AL, et al. Therapy of type 2 diabetes. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2019;127(Suppl 1):S73–92. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

