Yi-Nao-Jie-Yu Prescription Relieves Post-Stroke Depression by Mitigating Ferroptosis in Hippocampal Neurons Via Activating the Nrf2/GPX4/SLC7A11 Pathway
- PMID: 40214929
- PMCID: PMC11991945
- DOI: 10.1007/s11481-024-10167-1
Yi-Nao-Jie-Yu Prescription Relieves Post-Stroke Depression by Mitigating Ferroptosis in Hippocampal Neurons Via Activating the Nrf2/GPX4/SLC7A11 Pathway
Abstract
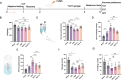
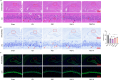
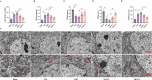
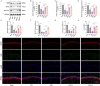
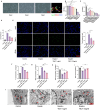
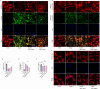
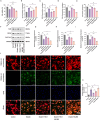
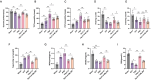
Post-stroke depression (PSD) poses a serious impact on patients' life quality. Effective drugs to treat this annoying disease are still being sought. Yi-nao-jie-yu (YNJY) prescription has been found to relieve PSD; however, the underlying mechanisms remain unelucidated. This work elucidated the therapeutic effects and mechanisms underlying YNJY prescription in PSD. PSD rat model was treated with YNJY prescription and ML385. Depression-like behaviors of rats was appraised. Hematoxylin-eosin, Nissl, and NeuN immunofluorescence staining were performed to observe hippocampal neuronal damage. Transmission electron microscopy was used to assess hippocampal mitochondrial damage. Commercial kits and western blotting were adopted to research ferroptosis-related factors and Nrf2/GPX4/SLC7A11 signals. In vitro experiments were performed using rat hippocampal neurons to explore the mechanism by which YNJY prescription relieves PSD. In PSD rats, YNJY prescription relieved depression-like behaviors, attenuated hippocampal neuronal damage, mitigated hippocampal ferroptosis and mitochondrial damage, and activated hippocampal Nrf2/GPX4/SLC7A11 pathway. By in vitro experiments, erastin treatment exacerbated hippocampal neuronal damage, ferroptosis, mitochondrial damage, and lipid peroxidation; however, YNJY prescription abolished these erastin-induced effects. In the erastin-treated hippocampal neuronal model of PSD, ML385 treatment increased ferroptosis, hippocampal neuronal damage, and lipid peroxidation; however, YNJY prescription counteracted these ML385-induced effects. By in vivo study, ML385 reversed the relief of YNJY prescription on depressive-like behaviors of PSD rats, and the inhibition on ferroptosis in PSD rats' hippocampus. YNJY prescription relieves PSD by blocking ferroptosis via activating the Nrf2/GPX4/SLC7A11 pathway. It may be a promising agent for treating PSD clinically.
Keywords: Ferroptosis; Hippocampal neurons; Nrf2/GPX4/SLC7A11; Post-stroke depression; Yi-nao-jie-yu prescription.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate: The Animal Committee of the MDKN Biotech Co. (Beijing, China) approved all animal studies (Approval No.: MDKN-2023–010). Furthermore, all animal experiments were conducted according to the “Guiding Opinions on the Good Treatment of Laboratory Animals” issued by the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Consent for Publication: Not applicable. Competing Interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bouvier E et al (2017) Nrf2-dependent persistent oxidative stress results in stress-induced vulnerability to depression. Mol Psychiatry 22(12):1701–1713 - PubMed
-
- Cao H et al (2021) Hippocampal proteomic analysis reveals activation of necroptosis and ferroptosis in a mouse model of chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression. Behav Brain Res 407:113261 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

