A digital motor score for sensitive detection of progression in Huntington's disease
- PMID: 40215265
- PMCID: PMC12404731
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awaf127
A digital motor score for sensitive detection of progression in Huntington's disease
Abstract
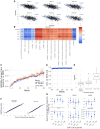
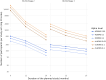
Remote digital monitoring of Huntington's disease (HD) has potential to enhance the development of therapeutics, but no data-driven digital motor score exists to quantify the diversity of disease manifestations and track their progression. The HD Digital Motor Score (HDDMS), co-designed with people with HD and neurologists, is a composite score for measuring motor progression of HD in clinical research. It is derived from smartphone sensor-based motor tests included in a remote HD digital monitoring platform. Developing the HDDMS involved selecting features that quantify test performance according to desired measurement properties and combining these features in a weighted composite score using factor analysis. It was developed and subsequently validated using data from four separate studies [HD Natural History Study (NCT03664804), open-label extension (OLE) of the tominersen phase I/IIa study (NCT03342053), GENERATION HD1 (NCT03761849) and Digital-HD]. Based on data from 1048 (the total number of individuals whose data contributed to the construction of the score includes the 40 gene-negative volunteers) individuals, the HDDMS encompasses balance, chorea, speeded tapping and gait. It has favourable characteristics, including reliability (intraclass correlation coefficient > 0.95), correlation with the composite Unified Huntington's Disease Rating Scale (cUHDRS) (r = -0.5), and better sensitivity to change (STC) than the cUHDRS. In a post hoc analysis of GENERATION HD1, the STC of HDDMS at Week 20 was comparable to that of the cUHDRS at Week 68. The HDDMS promises substantial reduction in sample size in clinical trials.
Keywords: digital health; digital health technology; disease progression; motor dysfunction; motor function; smartphone.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain.
Conflict of interest statement
L.-S.G. is a consultant for F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd via Efor Group. C.S. is an employee of F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. J.R. is a contractor for F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. A.B. is a consultant for F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd via Inovigate. F.C.K. is an employee of University College London. A.V.S. is an employee of Ionis Pharmaceuticals. P.M. is an employee of Roche Products Limited. M. Lindemann is a consultant for F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd via Inovigate. F.L. is an employee of F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. E.J.W. reports grants and personal fees from F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, grants from Medical Research Council UK and grants from CHDI Foundation during the conduct of the study; and personal fees from Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, PTC Therapeutics, Skyhawk Therapeutics, Teitur Trophics, Uniqure, Wave Life Sciences, Vico Therapeutics, Triplet Therapeutics, Mitoconix and Loqus outside the submitted work. J.D. is an employee of F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

