Psychological stress increases skin infection through the action of TGFβ to suppress immune-acting fibroblasts
- PMID: 40215323
- PMCID: PMC12183641
- DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.ads0519
Psychological stress increases skin infection through the action of TGFβ to suppress immune-acting fibroblasts
Abstract
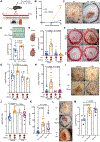
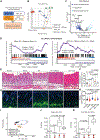
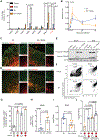
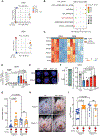
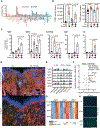
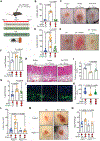
Infections after psychological stress are a major health care problem. Single-cell transcriptomics and lipidomic profiling in a mouse model of stress show that dermal fibroblasts undergoing adipogenesis have defective responses to Staphylococcus aureus skin infection. Adrenalectomy or adrenergic inhibition restores the fibroblast adipogenic response to S. aureus and enables mice to effectively resist infection during stress. Increased susceptibility to S. aureus from stress is attributed to suppression of the antimicrobial peptide cathelicidin (Camp) because adrenaline directly inhibits Camp production by fibroblasts, and mice lacking Camp in fibroblasts do not increase infection after stress. Transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) is induced by stress and adrenergic signaling, and inhibition of TGFβ or deletion of the TGFβ receptor on fibroblasts increases Camp expression and restores protection against infection. Together, these data show that stress initiates a brain-skin axis mediated by TGFβ that impairs the immune defense function of dermal fibroblasts to produce the Camp antimicrobial peptide.
Figures

References
-
- Barsotti N, Chiera M, Lanaro D, Fioranelli M, Impact of stress, immunity, and signals from endocrine and nervous system on fascia. Front. Biosci 13, 1–36 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Rojas I-G, Padgett DA, Sheridan JF, Marucha PT, Stress-induced susceptibility to bacterial infection during cutaneous wound healing. Brain Behav. Immun 16, 74–84 (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

