Unexplained breathlessness: Integrating pathophysiological insights with clinical evaluation
- PMID: 40216191
- PMCID: PMC12242847
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clinme.2025.100313
Unexplained breathlessness: Integrating pathophysiological insights with clinical evaluation
Abstract
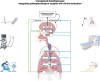
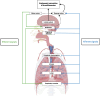
Unexplained breathlessness is a challenging symptom encountered across diverse medical conditions. This review will briefly overview the interplay between central neural mechanisms and peripheral receptor activity leading to symptom perception. A holistic and multidisciplinary approach to unexplained breathlessness is crucial to assess and optimise known comorbidities, as well as investigate potential less common conditions associated with dyspnoea. Specific advanced testing modalities will be briefly discussed in the context of breathing pattern disorders, laryngeal hyperreactivity, disorders of the pulmonary vasculature, autonomic dysfunction and cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: Cardiopulmonary exercise testing; Complex breathlessness; Exertional dyspnoea; Unexplained breathlessness.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pathophysiological mechanisms of exertional dyspnea in people with cardiopulmonary disease: Recent advances.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2025 Aug-Sep;336:104423. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2025.104423. Epub 2025 Mar 29. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40164293 Review.
-
The role of invasive cardiopulmonary exercise testing in patients with unexplained dyspnea: a systemic review.Acta Cardiol. 2023 Sep;78(7):754-760. doi: 10.1080/00015385.2022.2141434. Epub 2022 Nov 8. Acta Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 36345986
-
Benzodiazepines for the relief of breathlessness in advanced malignant and non-malignant diseases in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Oct 20;10(10):CD007354. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007354.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27764523 Free PMC article.
-
Benzodiazepines for the relief of breathlessness in advanced malignant and non-malignant diseases in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Jan 20;(1):CD007354. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007354.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Oct 20;10:CD007354. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007354.pub3. PMID: 20091630 Updated.
-
Opioids for the palliation of refractory breathlessness in adults with advanced disease and terminal illness.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 31;3(3):CD011008. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011008.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27030166 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Population-specific risk models and AI in clinical practice: Are we ready for the next step in managing common disorders?Clin Med (Lond). 2025 May;25(3):100329. doi: 10.1016/j.clinme.2025.100329. Epub 2025 May 17. Clin Med (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40389096 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- England NHS. NHS England » adult breathlessness pathway (pre-diagnosis): diagnostic pathway support tool. Accessed March 24, 2025. https://www.england.nhs.uk/long-read/adult-breathlessness-pathway-pre-di....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

