Tacrolimus versus cyclosporine immunosuppression in lung transplantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40216413
- PMCID: PMC11987090
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjresp-2024-002672
Tacrolimus versus cyclosporine immunosuppression in lung transplantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The relative efficacy of calcineurin inhibitors tacrolimus and cyclosporine in lung transplantation remains unclear. To clarify, we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods: We searched through EMBASE, MEDLINE and Cochrane CENTRAL until 23 October 2023 for randomised trials comparing tacrolimus with cyclosporine in lung transplant recipients. Data extraction and bias risk assessment were done independently. Analyses included random effects pairwise meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis, with GRADE system for evidence certainty.
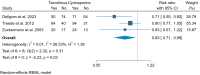
Results: We found four eligible trials totalling 662 patients. Tacrolimus significantly reduces the risk of chronic lung allograft dysfunction (RR 0.46, high certainty) and likely decreases acute rejection risk (RR 0.83, moderate certainty), with no clear difference in mortality (RR 1.08, low certainty). It may raise new-onset diabetes mellitus (RR 4.17, low certainty) and renal dysfunction risks (RR 1.27, low certainty).
Conclusion: Tacrolimus likely lowers acute rejection and chronic dysfunction risks in lung transplant recipients without improving survival rates. However, it might increase the chances of developing diabetes mellitus and renal dysfunction. These findings guide the choice between tacrolimus and cyclosporine, balancing benefits against potential risks.
Keywords: Lung Transplantation.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


References
-
- Chambers DC, Cherikh WS, Harhay MO, et al. The International Thoracic Organ Transplant Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: Thirty-sixth adult lung and heart-lung transplantation Report-2019; Focus theme: Donor and recipient size match. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2019;38:1042–55. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2019.08.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chambers DC, Perch M, Zuckermann A, et al. The International Thoracic Organ Transplant Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: Thirty-eighth adult lung transplantation report - 2021; Focus on recipient characteristics. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2021;40:1060–72. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2021.07.021. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
