Impact of aminoglycosides on survival rate and renal outcomes in patients with urosepsis: a multicenter retrospective study
- PMID: 40216650
- PMCID: PMC11992283
- DOI: 10.1186/s13613-025-01469-5
Impact of aminoglycosides on survival rate and renal outcomes in patients with urosepsis: a multicenter retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Combination therapy with a beta-lactam and an aminoglycoside is currently recommended for the empirical treatment of urosepsis. Nephrotoxicity is the most common adverse effect of aminoglycosides and acute kidney injury (AKI) has a significant prognostic impact in septic shock. This study aimed to evaluate the impact of empirical antibiotic therapy with or without an aminoglycoside on survival and renal outcomes in patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) with urosepsis.
Methods: This multicenter, retrospective, comparative study included all adults admitted to the ICU for urinary sepsis or septic shock between January 2015 and May 2022 in four ICUs of three university hospitals within the Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris (APHP). The primary outcome was mortality on day 30 after ICU admission. Secondary endpoints included the lack of renal recovery, the need for new renal replacement therapy (RRT), the Major Adverse Kidney Events at day 30 (MAKE 30) and ICU length of stay. Confounding by indication was taken into account using propensity score weighting.
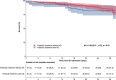
Results: A total of 580 patients were included, median age was 69 years (interquartile: 58-77) and 53.6% were male. Overall, 335 patients (57.8%) were in septic shock and 448 (79.2%) had AKI on admission. A total of 579 patients (99.8%) received a beta-lactam as empirical therapy (with (n = 444) or without (n = 136) aminoglycosides). The overall 30-day mortality rate was 10.5% (61/580). After propensity score weighting, the mortality rate in patients receiving aminoglycosides was 7.7% (7/91) compared to 12.1% (11/91) in those not receiving aminoglycosides (adjusted hazard ratio (aHR) = 0.65 [0.35; 1.23], p = 0.19). No significant differences were found in the lack of renal recovery at day 30 (aHR = 0.88 [0.49; 1.58], p = 0.67), the need for new RRT within 30 days (aHR = 1.01 [0.54; 1.88], p = 0.97), MAKE 30 (aHR = 0.94 [0.60; 1.50], p = 0.81), and ICU length of stay among survivors (aHR = 1.07 [0.87; 1.31], p = 0.53).
Conclusions: Including aminoglycosides in the empirical antibiotic therapy did not significantly improve 30-day survival in patients admitted to the ICU for urosepsis. However, the use of aminoglycosides was not associated with worse renal outcomes.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Aminoglycosides; Mortality; Septic shock; Urinary tract infections.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee for Infectious and Tropical Diseases (CER-MIT-2023-0503) in Paris, France, and was conducted in accordance with the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. Informed consent was not required due to the retrospective nature of the study, in accordance with the ethics committee and French law. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: ASL declared Lectures for Pierre Fabre, unrelated to this work. FD declared Lectures for Biomerieux, Gilead, and research grants from French Ministry of Health. JC declared SCYNEXIS and MSD unrelated with this work. DR, AM, RA, SB, JC, MD, VD, JLD, HJ, HP, and JMM declared no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- Levy MM, Artigas A, Phillips GS, et al. Outcomes of the surviving Sepsis Campaign in intensive care units in the USA and Europe: a prospective cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2012;12:919–24. 10.1016/S1473-3099(12)70239-6. - PubMed
-
- Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W, et al. Surviving sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock: 2016. Intens Care Med. 2017;43:304–77. 10.1007/s00134-017-4683-6. - PubMed
-
- Cariou E, Griffier R, Orieux A, et al. Efficacy of carbapenem vs. non carbapenem β-lactam therapy as empiric antimicrobial therapy in patients with extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacterales urinary septic shock: a propensity-weighted multicenter cohort study. Ann Intens Care. 2023;13:22. 10.1186/s13613-023-01106-z. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

