Development and validation of a novel endoplasmic reticulum stress-related lncRNA signature in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 40216868
- PMCID: PMC11992065
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-96576-5
Development and validation of a novel endoplasmic reticulum stress-related lncRNA signature in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
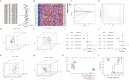
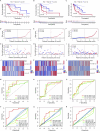
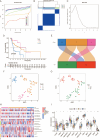
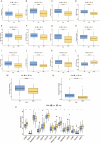
Endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) is an intracellular process in which improperly folded proteins lead to a cellular stress response. How endoplasmic reticulum stress contributes to the onset and progression of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma remains unclear. Our research aimed to find an ERS signature to forecast the prognosis of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma and to investigate its potential biological functions. LSCC sample data obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database were co-expressed with ERS- related genes, and then a prognostic signature on the basis of endoplasmic reticulum stress- related lncRNAs (ERS-related lncRNAs) was constructed by differential analysis and Cox regression analysis. Survival analysis, TMB, consensus cluster analysis, drug sensitivity analysis, immune analysis and clinical drug prediction were carried out on the model. Finally, the function of LHX1-DT was verified by in vitro experiments. From the TCGA-LSCC cohort, 35 significantly different ERS-related lncRNAs were identified. A prognostic signature consisting of three lncRNAs (AC110611.2, LHX1-DT, and AL157373.2) was identified. Kaplan-Meier analysis demonstrated the predictive ability of the model for overall survival. Calibration curves and receiver operating characteristic curves were validated and showed high predictive accuracy. Ultimately, the experimental results verified the expression of LHX1-DT in LSCC.
Keywords: Endoplasmic reticulum stress; Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma; LncRNA; Prognostic model.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Construction and validation of a prognostic signature based on seven endoplasmic reticulum stress-related lncRNAs for patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 16;13(1):22414. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-49987-1. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38104177 Free PMC article.
-
An immune-related lncRNA pairs signature to identify the prognosis and predict the immune landscape of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2022 May 14;22(1):545. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09524-1. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35568824 Free PMC article.
-
A novel endoplasmic reticulum stress-related lncRNA signature for prognosis prediction and immune response evaluation in Stomach adenocarcinoma.BMC Gastroenterol. 2023 Dec 9;23(1):432. doi: 10.1186/s12876-023-03001-0. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 38066437 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of differentially expressed profiles of lncRNAs, mRNAs, and miRNAs in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma in order to construct a ceRNA network and identify potential biomarkers.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Oct;120(10):17963-17974. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29063. Epub 2019 May 24. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31127661
-
Potentials of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA networks as biomarkers for laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.Hum Cell. 2023 Jan;36(1):76-97. doi: 10.1007/s13577-022-00799-x. Epub 2022 Oct 1. Hum Cell. 2023. PMID: 36181662 Review.
References
-
- Zhang, X. et al. Research progress on the interaction between oxidative stress and platelets: Another avenue for cancer?. Pharmacol. Res.191, 106777 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Li, S. et al. Exosomes: Another intercellular lipometabolic communication mediators in digestive system neoplasms?. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.73, 93–100 (2023). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

