Study on the regulatory mechanism of luteolin inhibiting WDR72 on the proliferation and metastasis of non small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 40216870
- PMCID: PMC11992086
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-96666-4
Study on the regulatory mechanism of luteolin inhibiting WDR72 on the proliferation and metastasis of non small cell lung cancer
Abstract
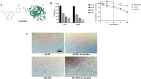
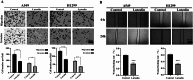
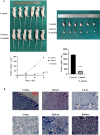
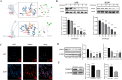
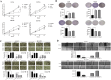
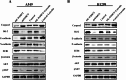
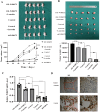
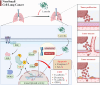
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a major cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide. Understanding molecular mechanisms and identifying potential therapeutic targets are crucial for improving treatment outcomes. This study aims to explore the effect of luteolin on NSCLC progression by regulating WDR72 and to investigate the related molecular mechanisms using cellular and animal models. The study employed a comprehensive set of experiments to evaluate the impact of luteolin and WDR72 on NSCLC cell proliferation and metastasis. Techniques included the CCK- 8 assay, colony formation assay, scratch test, and Transwell assay. Molecular docking experiments were performed to validate the binding interaction between luteolin and WDR72. Experimental groups included OE-WDR72, OE-WDR72 + Luteolin, Control, Control + Luteolin, and sh-WDR72. Western blot analysis was used to examine protein expression related to apoptosis, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), AKT signaling, and other markers. Additionally, a nude mouse subcutaneous tumor model was established to assess the in vivo tumor-forming ability of NSCLC cells under different treatments. Luteolin significantly inhibited the proliferation, invasion, and migration of NSCLC cell lines (H1299 and A549) and reduced tumor formation in nude mice. Molecular docking demonstrated strong binding affinity between luteolin and WDR72. Overexpression of WDR72 promoted NSCLC cell proliferation and migration, while WDR72 silencing showed the opposite effects. Western blot analysis revealed that WDR72 overexpression increased phosphorylated AKT and Bcl- 2 levels while decreasing caspase- 3. In contrast, silencing WDR72 reduced these protein levels. Luteolin treatment in WDR72-overexpressing cells resulted in decreased phosphorylated AKT, increased apoptosis, and suppressed EMT. Tumor transplantation experiments indicated that tumors in the OE-WDR72 group exhibited the fastest growth, while the sh-WDR72 group showed the slowest growth. Luteolin treatment significantly reduced WDR72 expression, suggesting a regulatory role in NSCLC progression. Luteolin effectively inhibits EMT, invasion, and migration of NSCLC cells by modulating WDR72. WDR72 plays a pivotal role in stimulating the proliferation and metastasis of NSCLC cells. By downregulating WDR72, luteolin suppresses NSCLC progression, potentially through modulation of the PI3 K/AKT/EMT signaling pathway. These findings highlight luteolin as a promising therapeutic agent for NSCLC treatment.
Keywords: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; Luteolin; Metastasis; Non-small cell lung cancer; Proliferation; Signaling pathway; WDR72.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval: This study was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Jiangsu Medical Vocational College (NO. SYLL- 2023 - 917) and followed the Declaration of Helsinki.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SSPH I, A Novel Anti-cancer Saponin, Inhibits EMT and Invasion and Migration of NSCLC by Suppressing MAPK/ERK1/2 and PI3K/AKT/ mTOR Signaling Pathways.Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2024;19(4):543-555. doi: 10.2174/0115748928283132240103073039. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2024. PMID: 38305308
-
Luteolin enhances drug chemosensitivity by downregulating the FAK/PI3K/AKT pathway in paclitaxel‑resistant esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Int J Mol Med. 2024 Sep;54(3):77. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2024.5401. Epub 2024 Jul 12. Int J Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38994756 Free PMC article.
-
Ophiopogonin B suppresses the metastasis and angiogenesis of A549 cells in vitro and in vivo by inhibiting the EphA2/Akt signaling pathway.Oncol Rep. 2018 Sep;40(3):1339-1347. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6531. Epub 2018 Jun 27. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29956803 Free PMC article.
-
The role of glutathione peroxidase 4 in the progression, drug resistance, and targeted therapy of non-small cell lung cancer.Oncol Res. 2025 Mar 19;33(4):863-872. doi: 10.32604/or.2024.054201. eCollection 2025. Oncol Res. 2025. PMID: 40191731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition: Biological Basis and Clinical Prospects of Lung Cancer Invasion, Metastasis, and Drug Resistance].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2025 Feb 20;28(2):155-164. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2025.102.07. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40114492 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Modulation of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Experimental Anti-Cancer Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 3;26(13):6407. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136407. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650182 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

