Regulation of MCCC1 expression by a Parkinson's disease-associated intronic variant: implications for pathogenesis
- PMID: 40216992
- PMCID: PMC12137145
- DOI: 10.1038/s10038-025-01335-z
Regulation of MCCC1 expression by a Parkinson's disease-associated intronic variant: implications for pathogenesis
Abstract
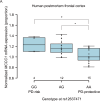
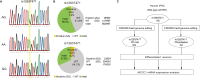
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a common neurodegenerative disorder characterized by dopaminergic neuron loss and α-synuclein aggregation. While some familial cases result from single-gene mutations, most are sporadic, involving complex genetic and environmental interactions. Among PD risk loci identified through genome-wide association studies, MCCC1 encodes a mitochondrial enzyme essential for leucine catabolism; however, the causal variant remains unclear. Here, we investigated whether the intronic variant rs12637471 regulates MCCC1 mRNA expression and influences PD risk. Postmortem brain analysis revealed significantly elevated MCCC1 mRNA levels in G-allele carriers, consistent with peripheral tissue eQTL data from GTEx. Using CRISPR/Cas9-edited induced pluripotent stem cells, we generated isogenic lines differing only at rs12637471 and observed increased MCCC1 expression in G-allele dopaminergic neurons. Given MCCC1's mitochondrial role, its dysregulation may impact mitochondrial homeostasis, autophagy, or inflammation, potentially contributing to PD pathogenesis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
