The role of imaging in endodontics
- PMID: 40217027
- PMCID: PMC11991906
- DOI: 10.1038/s41415-025-8511-z
The role of imaging in endodontics
Abstract
Dental radiography is an essential tool in endodontics for determination of diagnosis, treatment planning and monitoring of treatment outcome. Conventional two-dimensional imaging remains the most commonly used and the standard method of radiographic imaging in endodontics due to accessibility and low radiation exposure. The use of cone beam computed tomography is increasing worldwide due to the benefits of three-dimensional visualisation of the teeth under investigation and surrounding structures. Its use, however, should be considered on a case-by-case basis, taking into consideration the benefits and increased dose of radiation in line with published guidelines.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics declaration. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
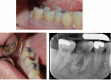
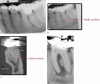
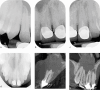
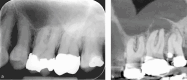
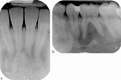
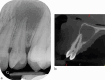
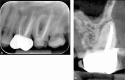
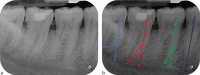
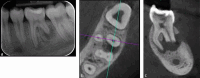
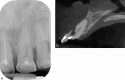
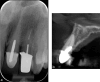


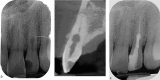
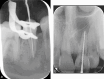

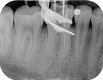

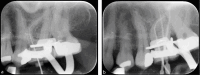
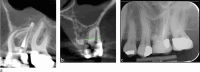
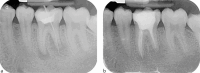
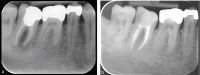
References
-
- Liang Y H, Li G, Wesselink P R, Wu M-K. Endodontic outcome predictors identified with periapical radiographs and cone-beam computed tomography scans. J Endod 2011; 37: 326-331. - PubMed
-
- Hubar J S, Caballero P. Localization of objects (SLOB Rule). In Hubar S, Caballero P (eds) Fundamentals of oral and maxillofacial radiology. pp 105-110. New Jersey: Wiley, 2017.
-
- Tai C C, Miller P A, Packota G V, Wood R E. The occlusal radiograph revisited. Oral Health 1994; 84: 47-53. - PubMed
-
- UK Government. Ionising radiation: dose comparisons. 2011. Available at https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/ionising-radiation-dose-compa... (accessed March 2025).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

