The nonlinear correlation of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio on 1-year mortality risk in patients with severe acute heart failure
- PMID: 40217135
- PMCID: PMC11987478
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-025-04734-4
The nonlinear correlation of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio on 1-year mortality risk in patients with severe acute heart failure
Abstract
Background: This retrospective cohort study was designed to examine the relationship between the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and the 1-year risk of death in patients with acute heart failure (AHF) in the intensive care unit (ICU).
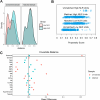
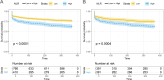
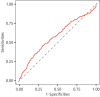
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 1,176 patients with AHF from the MIMIC-IV database. Cox regression was used to evaluate the relationship between NLR and 1-year mortality risk after adjusting for covariates. Nonlinear associations and optimal NLR cutoff values were determined using restricted cubic splines. Propensity score matching was used to eliminate imbalances in the baseline confounders. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis further confirmed the correctness of the threshold. The ROC was used to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of the NLR for long-term outcomes. Subgroup analyses were performed to assess the generality of NLR in specific populations.
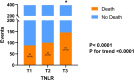
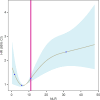
Results: The mortality rate was lowest in the lower tertile NLR group (< 5.43) and highest in the upper tertile group (> 13.53, P for trend < 0.001). NLR showed a nonlinear correlation with mortality (P for Non-linearity = 0.0075), with the risk increasing significantly when NLR exceeded 11.11. The AUC of NLR for predicting 1-year mortality was 0.579 (95%CI 0.542-0.617). The NLR was not significantly different from long-term outcomes in most groups, but the association was stronger in patients with AHF who did not have sepsis.
Conclusion: Elevated NLR, a marker of heightened systemic inflammation, was associated with a higher risk of 1-year mortality in ICU patients with AHF.
Clinical trial number: Not applicable.
Keywords: Acute heart failure; Intensive care unit; MIMIC IV; Neutrophil lymphocyte ratio.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The MIMIC-IV database systematically collected data from sepsis patients in the ICUs of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston, Massachusetts, USA, from 2008 to 2019. This project has received approval from the Institutional Review Boards of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center. This database is an open data set. Bo Liu, the corresponding author of this study, has completed the application and obtained the authorization (Record ID: 62175707). All health data of patients in this database have been de-identified, thereby obviating the need for obtaining informed consent from the patients. This study was conducted in accordance with the principles of the 2013 Helsinki Declaration. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The prognostic value of the combined neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and neutrophil-to-platelet ratio (NPR) in sepsis.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 2;14(1):15075. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64469-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38956445 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and the 90-day all-cause mortality in patients with acute respiratory failure: a retrospective analysis based on the MIMIC-IV Database.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025 Feb 18;25(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s12872-025-04553-7. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025. PMID: 39966744 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between the Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio and Prognosis of Patients Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit With Chronic Heart Failure: A Retrospective Cohort Study.Angiology. 2024 Sep;75(8):786-795. doi: 10.1177/00033197231196174. Epub 2023 Aug 16. Angiology. 2024. PMID: 37586709
-
Predictive role of neutrophil percentage-to-albumin ratio, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, and systemic immune-inflammation index for mortality in patients with MASLD.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 5;14(1):30403. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-80801-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39638820 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Predictor of Mortality and Clinical Outcomes in Heart Failure Patients.Cureus. 2025 May 2;17(5):e83359. doi: 10.7759/cureus.83359. eCollection 2025 May. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40452699 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tomasoni D, Lombardi CM, Sbolli M, Cotter G, Metra M. Acute heart failure: more questions than answers. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2020;63:599–606. - PubMed
-
- Gall E, Pezel T, Lattuca B, Hamzi K, Puymirat E, Piliero N et al. Profile of patients hospitalized in intensive cardiac care units in France: ADDICT-ICCU registry. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2024;:S1875-2136(24)00024-X. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

