Biomarkers in headaches as a potential solution to simplify differential diagnosis of primary headache disorders: a systematic review
- PMID: 40217141
- PMCID: PMC11987472
- DOI: 10.1186/s10194-025-02023-1
Biomarkers in headaches as a potential solution to simplify differential diagnosis of primary headache disorders: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: According to the International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (ICHD-3), headache disorders can be divided into two main groups: primary, which are not caused by any other disease, and secondary, which are symptomatic of underlying disease. Differentiating between both groups is crucial for the patient's prognosis. The diagnosis of primary headache disorders relies solely on official clinical criteria, with no additional diagnostic tools available. Therefore, they usually remain underdiagnosed, decreasing the patient's quality of life.
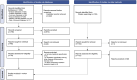
Methods: This systematic review aimed to analyse the available literature on the topic of biomarkers in the differentiation between different types of headaches. To be included, a primary study had to cover the abovementioned topic. Studies comparing one type of headache to healthy controls were excluded since the review focused on differential diagnosis. Articles to be considered had to describe original research and be written in English or Polish. No publication year limits were applied. A selection process was performed between October 19th, 2024, and January 1st, 2025, through six databases (PubMed, Embase, Scopus, Cochrane, Web of Science, Medline Ultimate), according to the PRISMA 2020. The risk of bias was assessed accordingly using the Prediction Model Risk of Bias Assessment Tool (PROBAST), and data synthesis was performed narratively. The review was registered in PROSPERO.
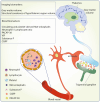
Findings: The findings from 21 included studies (with a wide range of publication years between 1990 and 2023) demonstrated several biomarkers, mainly comparing migraine to other primary headaches, tension-type headaches and cluster headaches, and some secondary headaches: medication-overuse headaches and post-traumatic headaches. The main types of biomarkers were blood biomarkers and imaging biomarkers. Among the former, molecules such as magnesium and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) or inflammatory markers could be found. The latter group focused mainly on assessing volumes or functional connections in brain magnetic resonance imaging and seem to have a significant impact in the nearest future. Saliva analyses were covered only by two research groups, showing the putative role of magnesium and CGRP. Similarly, two research groups described evoked potentials' value only in the paediatric population.
Conclusions: There is a clear gap in the literature regarding biomarkers for the differential diagnosis of headaches. However, an analysis of the most recent studies suggests that imaging biomarkers are the most promising group since they have gained the most attention in the past few years. Finding high-value biomarkers can simplify differential diagnosis of headaches, especially when clinical presentation is atypical. Nevertheless, more research on biomarkers of all types is highly needed.
Prospero: Registration ID: CRD42024603632.
Keywords: Biomarker; Cluster headaches; Differential diagnosis; Migraine; Primary headache disorders; Tension-type headaches; Trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Antidepressants for pain management in adults with chronic pain: a network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(62):1-155. doi: 10.3310/MKRT2948. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39367772 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Onderwater GLJ et al (2017) Primary headaches. Handb Clin Neurol 146:267–284 - PubMed
-
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS) The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia, (2018) 38(1): pp. 1-211 - PubMed
-
- Frederiksen SD (2019) Promote biomarker discovery by identifying homogenous primary headache subgroups. Headache 59(5):797–801 - PubMed
-
- Giamberardino MA et al (2020) Acute headache management in emergency department. A narrative review. Intern Emerg Med 15(1):109–117 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

