Neuroprotective role of morin hydrate on 3-nitropropionic acid-elicited huntington's disease: in vivo investigation of RIPK1/RIPK3/MLKL necroptosis signaling pathway
- PMID: 40217493
- PMCID: PMC11987198
- DOI: 10.1186/s10020-025-01172-y
Neuroprotective role of morin hydrate on 3-nitropropionic acid-elicited huntington's disease: in vivo investigation of RIPK1/RIPK3/MLKL necroptosis signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: Huntington's disease (HD) is a rare dominantly inheritable autosomal neurodegenerative disease with unclear pathophysiological pathways. In neurodegenerative disorders, including HD, necroptosis plays a significant role in neuronal death. Morin hydrate (MH), a natural bioactive flavonoid, has various pharmacological properties via orchestrating neuroinflammation, apoptosis, and necroptosis. Up to now, there is no extant data on the impact of MH on the necroptotic pathway in HD.
Aim: This research aimed to scrutinize the effect of MH on neurodegeneration initiated by 3-nitropropionic acid (3-NP) administration in rats via modulating necroptosis and apoptosis signaling pathways and compare it with necrosulfonamide (NSA) as a necroptosis inhibitor.
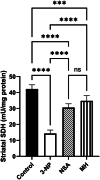
Methods: HD was triggered in male wistar rats by intraperitoneal injection of 3-NP (10 mg/kg/day) for 14 days. Intraperitoneal injection of MH (20 mg/kg/day, i.p.) or NSA (1.65 mg/kg/day, i.p.) an hour prior to 3-NP administration for 14 days. At the end of study, rats were weighed, and their locomotor activity was assessed via grip strength and open field tests. Striata of rats were investigated histologically and immunohistochemically by evaluation the expression levels of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). Striatal tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), caspase 3, and 8 levels were quantified through the ELISA technique, while striatal expression of necroptosis-associated proteins; phosphorylated form of receptor interacting protein kinase 1/3(p-RIPK1, p-RIPK3) and phosphorylated form of mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein (p-MLKL) were assessed by the Western blot technique. Striatal succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) activity was assayed colorimetrically. Finally, gene enrichment analysis using ShinyGO was employed.
Results: MH and NSA significantly mitigated body weight loss and ameliorated locomotor deterioration, besides reversing histological abnormalities in the striatum of rats. Intriguingly, MH exerted similar effects on specific biomarkers and molecular signals as NSA. MH and NSA inhibited neuroinflammation, apoptosis, and necroptosis by significantly decreasing the striatal (TNF-α), caspase 3, and necroptosis-associated proteins (P-RIPK1, P-RIPK3, and P-MLKL) levels. Besides, MH and NSA also decreased striatal GFAP and increased SDH activity. Gene enrichment analysis revealed a significant interaction between genes. Together, MH exerts a neuroprotective action on 3-NP-elicited HD rats via reducing neuroinflammation, apoptosis, and necroptosis. This study highlights MH as a potential protection against HD, calling for further research to confirm its neuroprotective effects.
Keywords: 3-nitropropionic acid; Huntington’s disease; Morin hydrate; Necroptosis; Necrosulfonamide.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study’s protocols were approved by the Ethics Committee for Animal Experimentation at the Faculty of Pharmacy, Cairo University (Permit Number: PT 3059). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Coniferaldehyde reverses 3-nitropropionic acid-induced Huntington's disease pathologies via PKM2 restoration and JAK2/STAT3 inhibition.Mol Med. 2025 Jul 31;31(1):271. doi: 10.1186/s10020-025-01308-0. Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40739177 Free PMC article.
-
Parthenolide ameliorates 3-nitropropionic acid-induced Huntington's disease-like aberrations via modulating NLRP3 inflammasome, reducing microglial activation and inducing astrocyte shifting.Mol Med. 2024 Sep 26;30(1):158. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00917-5. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39327568 Free PMC article.
-
Oxytocin Anti-Apoptotic Potential Mediates Neuroprotection Against 3-Nitropropionic Acid-Induced Huntington's Disease-Like Pathophysiology in Rats: Involvement of Calpain-2/p25 Cdk5/MEF-2 Signaling Pathway.Neurochem Res. 2025 Apr 19;50(3):148. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04397-9. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 40252127
-
RIPK1 in necroptosis and recent progress in related pharmaceutics.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 11;16:1480027. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1480027. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40007541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From RIPK1 to Necroptosis: Pathogenic Mechanisms in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Neurochem Res. 2025 Jun 10;50(3):194. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04448-1. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 40493155 Review.
Cited by
-
Coniferaldehyde reverses 3-nitropropionic acid-induced Huntington's disease pathologies via PKM2 restoration and JAK2/STAT3 inhibition.Mol Med. 2025 Jul 31;31(1):271. doi: 10.1186/s10020-025-01308-0. Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40739177 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abd El-Aal SA, El-Abhar HS, Abulfadl YS. Morin offsets PTZ-induced neuronal degeneration and cognitive decrements in rats: The modulation of TNF-α/TNFR-1/RIPK1,3/MLKL/PGAM5/Drp-1, IL-6/JAK2/STAT3/GFAP and Keap-1/Nrf-2/HO-1 trajectories. Eur J Pharmacol. 2022;931. 10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.175213. - PubMed
-
- Abdelhady R, Younis NS, Ali O, Shehata S, Sayed RH, Nadeem RI. Cognitive enhancing effects of pazopanib in D–galactose/ovariectomized Alzheimer’s rat model: insights into the role of RIPK1/RIPK3/MLKL necroptosis signaling pathway. Inflammopharmacology. 2023;31:2719–29. 10.1007/s10787-023-01269-y. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmed LA, Darwish HA, Abdelsalam RM, Amin HAA. Role of Rho kinase Inhibition in the protective effect of fasudil and Simvastatin against 3-Nitropropionic Acid-Induced striatal neurodegeneration and mitochondrial dysfunction in rats. Mol Neurobiol. 2016;53:3927–38. 10.1007/s12035-015-9303-2. - PubMed
-
- Almeida S, Brett AC, Góis IN, Oliveira CR, Rego AC. Caspase-dependent and -independent cell death induced by 3-nitropropionic acid in rat cortical neurons. J Cell Biochem. 2006;98:93–101. 10.1002/jcb.20748. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

