Autophagy-related genes in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy: an integrated bioinformatics analysis
- PMID: 40217519
- PMCID: PMC11960276
- DOI: 10.1186/s42494-024-00160-9
Autophagy-related genes in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy: an integrated bioinformatics analysis
Abstract
Background: Autophagy plays essential roles in the development and pathogenesis of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy (mTLE). In this research, we aim to identify and validate the autophagy-related genes associated with mTLE through bioinformatics analysis and experimental validations.
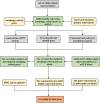
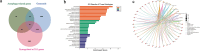
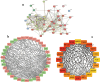
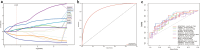
Methods: We obtained the dataset GSE143272 and high-throughput sequencing results of mTLE from public databases. Potential differentially expressed autophagy-related genes related to mTLE were identified using R software. Subsequently, genomes pathway enrichment analysis, protein-protein interactions (PPIs), and the gene ontology (GO) enrichment were performed for the selected autophagy-related genes. The mRNA expression profiles of hub genes were then used to establish a least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) model. Finally, seven hub candidate autophagy-related genes were confirmed in hippocampus using the lithium-pilocarpine chronic epilepsy model.
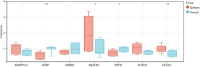
Results: A total of 40 differential expression genes (DEGs) among the core autophagy-related genes were identified. The analysis results of PPI revealed that interactions among these DEGs. KEGG pathway and GO analysis of selected candidate autophagy-related genes indicated that those enriched terms mainly focused on macroautophagy, regulation of autophagy, cellular response to extracellular stimulus and mitochondrion disassembly. The results suggested that SQSTM1, VEGFA, BNIP and WIPI2 were consistent with the bioinformatics analysis. The expression levels of SQSTM1 and VEGFA in epilepsy model samples were significantly higher than those in normal control, while BNIP and WIPI2 expression levels were notably decreased. The final hub gene-based LASSO regression model accurately predicted the occurrence of epilepsy (AUC = 0.88).
Conclusions: Through bioinformatics analysis of public data, we identified 40 candidate autophagy-related genes associated with mTLE. SQSTM1, VEGFA, BNIP and WIPI2 may play significant roles in autophagy, influencing the onset and development of mTLE by regulating autophagy pathway. These findings deepen our understanding of mTLE, and may serve as sensitive and valuable indicators for the prognosis and diagnosis of this condition.
Keywords: Autophagy; Bioinformatics analysis; Biomarkers; Mesial temporal lobe epilepsy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee, Sun Yat-Sen University (Approval No. SYSU-IACUC-2022-B1339). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: Author Liemin Zhou is the member of the Editorial Board for Acta Epileptologica, who was not involved in the journal’s review of, or decisions related to this manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of Ion Channel-Related Genes and miRNA-mRNA Networks in Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy.Front Genet. 2022 Mar 29;13:853529. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.853529. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35422840 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Hub Genes of Mesio Temporal Lobe Epilepsy and Prognostic Biomarkers of Brain Low-grade Gliomas Based on Bioinformatics Analysis.Cell Transplant. 2020 Jan-Dec;29:963689720978722. doi: 10.1177/0963689720978722. Cell Transplant. 2020. PMID: 33327771 Free PMC article.
-
To establish and validate autophagy related biomarkers for the diagnosis of IgA nephropathy.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 22;15(1):13944. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-98591-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40263537 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of potential autophagy-related genes in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head via bioinformatics analysis and experimental verification.J Orthop Surg Res. 2022 Feb 12;17(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-02977-x. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022. PMID: 35151359 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture Promotes Autophagy by Regulating the AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy.Neurochem Res. 2022 Aug;47(8):2396-2404. doi: 10.1007/s11064-022-03634-9. Epub 2022 May 27. Neurochem Res. 2022. PMID: 35622215
References
-
- Giorgi FS, Biagioni F, Lenzi P, Frati A, Fornai F. The role of autophagy in epileptogenesis and in epilepsy-induced neuronal alterations. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2015;122(6):849–62. - PubMed
-
- Henske EP, Jozwiak S, Kingswood JC, Sampson JR, Thiele EA. Tuberous sclerosis complex. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16035. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
