Endotyping Insulin-Glucose Homeostasis in Hidradenitis Suppurativa: The Impact of Diabetes Mellitus and Inflammation
- PMID: 40217596
- PMCID: PMC11990022
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14072145
Endotyping Insulin-Glucose Homeostasis in Hidradenitis Suppurativa: The Impact of Diabetes Mellitus and Inflammation
Abstract
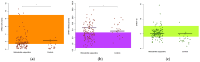
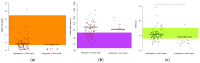
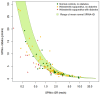
Background: Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory skin disease often associated with metabolic disorders such as diabetes mellitus. Recent research suggests a link between systemic inflammation and insulin-glucose dysregulation in HS. This study investigates the relationship between insulin-glucose homeostasis, diabetes mellitus and the haptoglobin concentration in HS patients. Methods: We assessed 95 HS patients and 49 controls using validated fasting-based function tests, including the Structural Parameter Inference Approach (SPINA), Homeostasis Model Assessment (HOMA) and Quantitative Insulin Sensitivity Check Index (QUICKI). Results: The HS patients had a significantly higher fasting insulin concentration (97.2 vs. 69.0 pmol/L, p = 0.035), increased insulin resistance (HOMA-IR: 3.47 vs. 2.57, p = 0.016) and impaired insulin sensitivity (SPINA-GR: 1.34 vs. 1.76 mol/s, p = 0.017). In diabetes, the insulin sensitivity was more strongly reduced (SPINA-GR: 0.61 vs. 1.41 mol/s, p = 0.0057) and the insulin resistance increased (HOMA-IR: 7.3 vs. 3.2, p = 0.017). Higher haptoglobin concentrations were accompanied by worse glycaemic control, demonstrating a significantly elevated fasting glucose (5.77 vs. 5.11 mmol/L, p = 0.043) concentration and HbA1c (5.7% vs. 5.4%, p = 0.0081) fraction. Conclusions: Our findings suggest that chronic inflammation in HS contributes to metabolic dysregulation, worsening insulin resistance and glycaemic control, particularly in those with elevated haptoglobin or diabetes.
Keywords: HOMA-IR; HS; dermato-endocrinology; hidradenitis suppurativa; insulin resistance; insulin–glucose homeostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
N.A. received funding, travel support, and/or personal honoraria for lectures from Novartis Pharma, Recordati Rare Diseases Germany GmbH, Janssen-Cilag GmbH and Johnson & Johnson that were independent of the work submitted. T.G. has received speaker and/or advisory board honoraria from BMS, Sanofi-Genzyme, MSD, Novartis Pharma, Roche, Abbvie, Almirall, Janssen, Lilly, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, and Merck-Serono outside the submitted work. F.G.B. has received honoraria for participation in advisory boards, in clinical trials, and/or as a speaker from AbbVie Inc., AbbVie Deutschland GmbH & Co. KG, Acelyrin, Beiersdorf, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co. KG, Celltrion, Dr. Wolff, Incyte Corporation, Janssen-Cilag GmbH, Johnson & Johnson, Merck, Mölnlycke, MoonLake, Novartis Pharma GmbH, Sanofi, Sitala and UCB Pharma. E.S. has received lecture fees from Almirall, Leo, Pierre Favre and Philips. L.O. has received honoraria as a speaker and/or travel support from Novartis Pharma GmbH, Incyte Biosciences Corporation and Janssen. J.W.D. received funding and personal fees from Novo Nordisk, VitalAire, Abbott, Medtronic, Oviva, myhomecare, Aidhere, Ascensia Diabetes Care, Sanofi-Henning, Hexal AG, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Egetis Therapeutics and Pfizer and is the co-owner of the intellectual property rights for the patent “System and Method for Deriving Parameters for Homeostatic Feedback Control of an Individual” (Singapore Institute for Clinical Sciences, Biomedical Sciences Institutes, Application Number 201208940-5, WIPO number WO/2014/088516). All the other authors (D.M. and Y.H.) declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Insulin resistance in hidradenitis suppurativa: a case-control study.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018 May;32(5):820-824. doi: 10.1111/jdv.14894. Epub 2018 Mar 23. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018. PMID: 29485215
-
Visfatin and insulin levels and cigarette smoking are independent risk factors for hidradenitis suppurativa: a case-control study.Arch Dermatol Res. 2018 Dec;310(10):785-793. doi: 10.1007/s00403-018-1867-z. Epub 2018 Oct 6. Arch Dermatol Res. 2018. PMID: 30293125
-
Neither homeostasis model assessment nor quantitative insulin sensitivity check index can predict insulin resistance in elderly patients with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002 Nov;87(11):5332-5. doi: 10.1210/jc.2002-020486. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002. PMID: 12414910
-
Probiotics improve renal function, glucose, lipids, inflammation and oxidative stress in diabetic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ren Fail. 2022 Dec;44(1):862-880. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2022.2079522. Ren Fail. 2022. PMID: 35611435 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics and pregnancy outcomes of subtypes of gestational diabetes mellitus based on HOMA-IR and BMI.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2024 Nov;310(5):2355-2361. doi: 10.1007/s00404-024-07733-6. Epub 2024 Sep 17. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2024. PMID: 39287682 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunohistochemical Expression of Haptoglobin in Skin Lesions of Hidradenitis Suppurativa.Life (Basel). 2025 May 2;15(5):738. doi: 10.3390/life15050738. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430166 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ballard K., Shuman V.L. Hidradenitis Suppurativa. StatPearls; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2025.
-
- Sabat R., Alavi A., Wolk K., Wortsman X., McGrath B., Garg A., Szepietowski J.C. Hidradenitis suppurativa. Lancet. 2025;405:420–438. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

