Assessment of Quality of Life of Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes in Bahrain Using PedsQL 3.2 Diabetes Module
- PMID: 40217667
- PMCID: PMC11989631
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14072216
Assessment of Quality of Life of Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes in Bahrain Using PedsQL 3.2 Diabetes Module
Abstract
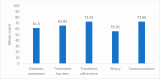
Background/Objectives: Living with type 1 diabetes (T1D) significantly impacts children and adolescents, affecting their physical, emotional, and social well-being. Poor glycemic control (HbA1c > 7.5%) is linked to lower health-related quality of life (HRQoL), highlighting the need for effective management. This study aimed to assess the HRQoL and evaluate the associations between various factors and domains of HRQoL among children and adolescents with T1D in Bahrain. Methods: This cross-sectional study enrolled 182 children and adolescents from 5 to 16 years with T1D from a tertiary care hospital. Participants had T1D for at least six months and were interviewed during regular follow-ups. Participants Outside the target age group and those with any comorbidity were excluded. Data collection involved demographic and diabetes-related information. The PedsQL 3.2 Diabetes Module was used to assess HRQoL. Results: The mean age at diagnosis was 6.83 ± 3.11 years, with 57.7% diagnosed between 6 and 11 years. The sample was gender-balanced (52.2% male, 47.8% female). Treatment adherence had the highest median score (80.0), while worry was the lowest (58.33). Diabetes symptoms were associated with family income, school performance, HbA1c, and emergencies. Treatment barriers were linked to age, education, insulin regimen, and glucometer type. Adherence correlated with age, age at diagnosis, sex, BMI, education, and comorbidities, with family income (β = 4.69, p = 0.032) and school performance (β = -22.986, p < 0.001) being significant predictors. Treatment adherence was negatively impacted by younger age (β = -20.651 for 6-8 years, β = -12.002 for 9-12 years, both p < 0.01) and comorbidities (β = -12.286, p = 0.021). Conclusions: This study highlights the significant impact of various factors on the HRQoL of children and adolescents with T1D in Bahrain, emphasizing the need for targeted interventions to improve their overall well-being.
Keywords: Bahrain; adolescent; child; diabetes mellitus; health-related quality of life; quality of life; type 1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Health-Related Quality of Life of Adolescents and Children With Type 1 Diabetes in the Jazan Region of Saudi Arabia.Cureus. 2024 Jan 31;16(1):e53307. doi: 10.7759/cureus.53307. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38435866 Free PMC article.
-
The associations between physical activity, health-related quality of life, regimen adherence, and glycemic control in adolescents with type 1 diabetes: A cross-sectional study.Prim Care Diabetes. 2023 Aug;17(4):392-400. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2023.04.003. Epub 2023 Apr 18. Prim Care Diabetes. 2023. PMID: 37080862
-
Health-related quality of life of children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes during the COVID-19 pandemic in Kuwait.Front Public Health. 2022 Dec 23;10:1056967. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1056967. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36620301 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of glycemic control in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes at 12 months after diagnosis.Pediatr Diabetes. 2022 Sep;23(6):729-735. doi: 10.1111/pedi.13342. Epub 2022 Apr 20. Pediatr Diabetes. 2022. PMID: 35393709 Review.
-
Psychological interventions to improve self-management of type 1 and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2020 Jun;24(28):1-232. doi: 10.3310/hta24280. Health Technol Assess. 2020. PMID: 32568666 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hilliard M.E., Minard C.G., Marrero D.G., de Wit M., Thompson D., DuBose S.N., Verdejo A., Monzavi R., Wadwa R.P., Jaser S.S., et al. Assessing Health-Related Quality of Life in Children and Adolescents with Diabetes: Development and Psychometrics of the Type 1 Diabetes and Life (T1DAL) Measures. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2020;45:328–339. doi: 10.1093/jpepsy/jsz083. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Murillo M., Bel J., Perez J., Corripio R., Carreras G., Herrero X., Mengibar J.M., Rodriguez-Arjona D., Ravens-Sieberer U., Raat H., et al. Health-related quality of life (HRQOL) and its associated factors in children with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM) BMC Pediatr. 2017;17:16. doi: 10.1186/s12887-017-0788-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources