Quantitative Evaluation of Kidney and Gallbladder Stones by Texture Analysis Using Gray Level Co-Occurrence Matrix Based on Diagnostic Ultrasound Images
- PMID: 40217718
- PMCID: PMC11989498
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14072268
Quantitative Evaluation of Kidney and Gallbladder Stones by Texture Analysis Using Gray Level Co-Occurrence Matrix Based on Diagnostic Ultrasound Images
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Accurate diagnosis during ultrasound examinations of patients with kidney and gallbladder stones is crucial. Although stone areas typically show posterior acoustic shadowing on ultrasound images, their accurate diagnosis can be challenging if the shaded areas are vague. This study proposes a method to improve the diagnostic accuracy of kidney and gallbladder stones through texture analysis of ultrasound images. Methods: Two doctors and three sonographers evaluated abdominal ultrasound images and categorized kidney and gallbladder stones into groups based on their predicted likelihood of being present: 50-60%, 60-80%, and ≥80%. The texture analysis method for the posterior acoustic shadows generated from ultrasound images of stones was modeled using a gray level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM). Average values and 95% confidence intervals were used to evaluate the method. Results: The three prediction classes were clearly distinguished when GLCMContrast was applied to the ultrasound images of patients with kidney and gallbladder stones. However, GLCMCorrelation, GLCMEnergy, and GLCMHomogeneity were found to be difficult for analyzing the texture of shadowed areas in ultrasound images because they did not clearly or completely distinguish between the three classes. Conclusions: Accurate diagnosis of kidney and gallbladder stones may be possible using the GLCM texture analysis method applied to ultrasound images.
Keywords: diagnostic ultrasound image; gray level co-occurrence matrix; kidney and gallbladder stones; posterior acoustic shadow; texture analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

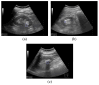
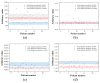

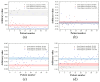
Similar articles
-
A survey of testicular texture in canine ultrasound images.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Aug 11;10:1206916. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1206916. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37635758 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of methods for texture analysis of QUS parametric images in the characterization of breast lesions.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 31;15(12):e0244965. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0244965. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33382837 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Gray Level Co-Occurrence Matrix-Based Texture Features of Magnetic Resonance Images for Glioblastoma Multiform Patients' Treatment Response Assessment.J Med Signals Sens. 2023 Aug 31;13(4):261-271. doi: 10.4103/jmss.jmss_50_22. eCollection 2023 Oct-Dec. J Med Signals Sens. 2023. PMID: 37809020 Free PMC article.
-
Management of urinary stones: state of the art and future perspectives by experts in stone disease.Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2024 Jun 27;96(2):12703. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2024.12703. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2024. PMID: 38934520 Review.
-
Texture Analysis in Musculoskeletal Ultrasonography: A Systematic Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Feb 21;15(5):524. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15050524. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40075772 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yamaguchi A., Kato N., Sugata S., Hamada T., Furuya N., Mizumoto T., Tamaru Y., Kusunoki R., Kuwai T., Kouno H., et al. Effectiveness of abdominal ultrasonography for improving the prognosis of pancreatic cancer during medical checkup: A Single Center retrospective analysis. Diagnostics. 2022;12:2913. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12122913. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arienti V., Aluigi L., Pretolani S., Accogli E., Polimeni L., Domanico A., Violi F. Ultrasonography (US) and non-invasive diagnostic methods for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and early vascular damage. Possible application in a population study on the metabolic syndrome (MS) Intern. Emerg. Med. 2012;7((Suppl. S3)):S283–S290. doi: 10.1007/s11739-012-0824-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Moftakhar L., Jafari F., Johari M.G., Rezaeianzadeh R., Hosseini S.V., Rezaianzadeh A. Prevalence and risk factors of kidney stone disease in population aged 40-70 years old in Kharameh cohort study: A cross-sectional population-based study in southern Iran. BMC Urol. 2022;22:205. doi: 10.1186/s12894-022-01161-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

