Remote Monitoring of Patients with Retinal Vein Occlusions Treated with Anti-VEGF: A Pilot Study
- PMID: 40217781
- PMCID: PMC11989553
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14072330
Remote Monitoring of Patients with Retinal Vein Occlusions Treated with Anti-VEGF: A Pilot Study
Abstract
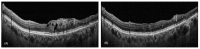
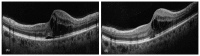
Purpose: To assess the feasibility and effectiveness of remote monitoring for patients with retinal vein occlusion (RVO) treated with intravitreal anti-VEGF injections. Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted at the Eye Clinic of the University of Catania. Thirty-four eyes of 34 patients with RVO were included for a 12-month follow-up period. After a comprehensive baseline ophthalmic examination, the patients received a loading treatment consisting of three monthly intravitreal injections of anti-VEGF, followed by monthly or bimonthly remote follow-up visits at peripheral centers. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) images and clinical data were shared online with our eye clinic for remote evaluations. Data on hospital and peripheral center visits, intravitreal injections, and OCT scans were collected and analyzed. Results: The patients had an average of 5.71 ± 1.14 visits to peripheral centers and 2.1 ± 0.8 visits to our center for fluorescein angiography. The mean number of injections was 5.26 ± 1.29 and the mean improvement in best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) was 11.47 ± 5.56 letters. Remote OCT evaluations accounted for 194 scans, there was a high agreement between two expert in-hospital examinators (Cohen's κ = 0.927) with only 14 cases requiring hospital visits for inconclusive results. Conclusions: Remote monitoring for RVO patients significantly reduced hospital admissions for follow-up visits, reducing the clinical burden on medical staff, patients, and caregivers, while maintaining reliable patient assessments.
Keywords: anti-VEGF; macular edema; optical coherence tomography; retinal vein occlusion; telemedicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Real life retrospective study of 98 eyes treated with intravitreal dexamethasone or anti-VEGF injections for macular edema due to diabetes or retinal vein occlusion].J Fr Ophtalmol. 2021 Oct;44(8):1148-1158. doi: 10.1016/j.jfo.2020.11.033. Epub 2021 Aug 2. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2021. PMID: 34353656 French.
-
Real-World Outcomes of Ranibizumab Treatment in French Patients with Visual Impairment due to Macular Edema Secondary to Retinal Vein Occlusion: 24-Month Results from the BOREAL-RVO Study.Ophthalmic Res. 2023;66(1):824-834. doi: 10.1159/000530294. Epub 2023 Mar 27. Ophthalmic Res. 2023. PMID: 36972579
-
Intravitreal bevacizumab (avastin) for central and hemicentral retinal vein occlusions: IBeVO study.Retina. 2007 Feb;27(2):141-9. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0b013e31802eff83. Retina. 2007. PMID: 17290194
-
Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor for macular oedema secondary to branch retinal vein occlusion.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jul 7;7(7):CD009510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009510.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32633861 Free PMC article.
-
Intravitreal Injection of Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factors Combined with Corticosteroids for the Treatment of Macular Edema Secondary to Retinal Vein Occlusion: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Semin Ophthalmol. 2024 Jan;39(1):109-119. doi: 10.1080/08820538.2023.2249527. Epub 2023 Aug 24. Semin Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 37621098
References
-
- Blair K., Czyz C.N. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2023. Central Retinal Vein Occlusion.
-
- Rogers S., McIntosh R.L., Cheung N., Lim L., Wang J.J., Mitchell P., Kowalski J.W., Nguyen H., Wong T.Y., International Eye Disease Consortium The prevalence of retinal vein occlusion: Pooled data from population studies from the United States, Europe, Asia, and Australia. Ophthalmology. 2010;117 doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2009.07.017. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

