A Protocol for a Systematic Review on Septic Arthritis of the Temporomandibular Joint (SATMJ)
- PMID: 40217842
- PMCID: PMC11989331
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14072392
A Protocol for a Systematic Review on Septic Arthritis of the Temporomandibular Joint (SATMJ)
Abstract
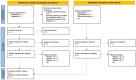
Background/Objectives: Septic arthritis of the temporomandibular joint is an infectious disease with a rapid course and possible long-term complications. It is crucial to diagnose and implement treatment quickly and to know the potential causes of the occurrence of SATMJ. The planned systematic review aims to summarize current knowledge on this subject. Methods: This protocol follows the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines and checklist. The following scientific databases will be searched: ACM, BASE, ClinicalTrials.gov, Cochrane Library, Google Scholar, PubMed, and Scopus. Studies on SATMJ that are consistent with the pre-established PICOTS criteria will be included in the systematic review. Two authors will independently conduct the record screening, data extraction, and quality appraisal phases. The quality of the studies will be evaluated using the JBI critical appraisal tools. Certainty assessment will be conducted using the GRADE tool. The obtained research results and data will be used to define and establish the current scientific position on the diagnosis and treatment of SATMJ. Conclusions on the lack of association of gender, age, and race with the occurrence of this disease entity will be verified, among others. The planned systematic review will be based on extensive searches for studies with no high risk of bias. The aim is to assist clinicians in managing SATMJ, and to inspire future research.
Keywords: protocol; septic arthritis; systematic review; temporomandibular disorders; temporomandibular joint.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Overview of Systematic Reviews on Septic Arthritis of the Temporomandibular Joint (SATMJ).J Clin Med. 2025 Jan 27;14(3):835. doi: 10.3390/jcm14030835. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 39941506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Septic arthritis of the temporomandibular joint in adults: Systematic review.J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2022 Sep;123(4):465-472. doi: 10.1016/j.jormas.2021.09.015. Epub 2021 Oct 7. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2022. PMID: 34628098
-
Acute septic arthritis of the temporomandibular joint derived from otitis media: a report and review of the English and Japanese literature.Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017 Mar;21(1):83-85. doi: 10.1007/s10006-016-0604-z. Epub 2016 Dec 5. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017. PMID: 27917456 Review.
-
The effectiveness of manual therapy applied to craniomandibular structures in the treatment of temporomandibular disorders: protocol for a systematic review.Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 8;10(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s13643-021-01623-7. Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33685496 Free PMC article.
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
References
-
- Lee Y.-H. Functional Anatomy of the Temporomandibular Joint and Pathologic Changes in Temporomandibular Disease Progression: A Narrative Review. J. Korean Dent. Sci. 2024;17:14–35. doi: 10.5856/JKDS.2024.17.1.14. - DOI
-
- Bliźniak F., Chęciński M., Chęcińska K., Lubecka K., Kamińska M., Szuta M., Chlubek D., Sikora M. Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Administered Intra-Articularly in Temporomandibular Joint Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2024;13:4056. doi: 10.3390/jcm13144056. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources