Prefrontal Cortical Near-Infrared Spectroscopy for Acute Pain Assessment in Infants: A Feasibility Study
- PMID: 40217972
- PMCID: PMC11989543
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14072525
Prefrontal Cortical Near-Infrared Spectroscopy for Acute Pain Assessment in Infants: A Feasibility Study
Abstract
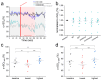
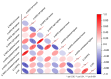
Background: Assessing pain in infants is challenging due to their inability to communicate discomfort. Accurate pain evaluation is essential, as unaddressed pain might lead to long-term neurological consequences. This study investigates the use of conventional two-site near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) to evaluate hemodynamic responses in the prefrontal cortex during nociceptive stimuli. Methods: Data were prospectively collected from ten infants undergoing elective heel lance/squeeze (HLS) after surgery. Continuous bilateral NIRS oxygenation monitoring was performed alongside cardiorespiratory and behavioral (Children's and Infant's Postoperative Pain Score (CHIPPS)) pain assessments before, during, and after HLS. The primary outcome was the correlation between NIRS response and CHIPPS. Results: The average gestational and postnatal ages were 39 weeks and 49 days. No significant changes in prefrontal oxygenation levels (left, right, combined, ipsilateral, contralateral) were observed during the first ten seconds of HLS compared with baseline. Although CHIPPS and heart rates increased, oxygenation levels remained unchanged throughout the entire HLS event. Significant fluctuations in oxygenation levels from baseline were recorded across all optode configurations, with changes in the lowest oxygenation levels at the contralateral and left hemispheres inversely correlated with CHIPPS and HR changes. Conclusions: While there were subtle alterations in NIRS signals suggesting potential nociceptive-evoked changes, these were inconclusive. By design, the utilized two-site conventional NIRS system may not effectively detect acute pain. Future studies on prefrontal cortical pain processing could benefit from confirmatory NIRS signals from the primary somatosensory and motor regions. Integrating data from fNIRS, fMRI, EEG, along with sympathetic indicators like skin conductance and heart rate variability, would improve the quantification of cortical pain processing in non-verbal infants.
Keywords: NIRS; bilateral frontal near-infrared spectroscopy; cerebral hemodynamics; heel/lance squeeze; infants; nociceptive stimulus; pain assessment; pediatric surgery; personalized interventions; prefrontal cortex; surgical pain management.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the study design; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Cerebral Hemodynamic Response to Pain in Preterm Infants With Fetal Growth Restriction.Front Pediatr. 2020 May 27;8:268. doi: 10.3389/fped.2020.00268. eCollection 2020. Front Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32537447 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebral near-infrared spectroscopy as a measure of nociceptive evoked activity in critically ill infants.Pain Res Manag. 2011 Sep-Oct;16(5):331-6. doi: 10.1155/2011/891548. Pain Res Manag. 2011. PMID: 22059205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Near infrared spectroscopy: experience on esophageal atresia infants.J Pediatr Surg. 2014 Jul;49(7):1064-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2014.01.010. Epub 2014 Jan 31. J Pediatr Surg. 2014. PMID: 24952789
-
Pain Induced Changes in Brain Oxyhemoglobin: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Functional NIRS Studies.Pain Med. 2021 Jun 4;22(6):1399-1410. doi: 10.1093/pm/pnaa453. Pain Med. 2021. PMID: 33659994
-
Near infrared spectroscopy--investigations in neurovascular diseases.Dan Med J. 2015 Dec;62(12):B5166. Dan Med J. 2015. PMID: 26621402
References
-
- Doesburg S.M., Chau C.M., Cheung T.P.L., Moiseev A., Ribary U., Herdman A.T., Miller S.P., Cepeda I.L., Synnes A., Grunau R.E. Neonatal Pain-Related Stress, Functional Cortical Activity and Visual-Perceptual Abilities in School-Age Children Born at Extremely Low Gestational Age. Pain. 2013;154:1946–1952. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2013.04.009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Grunau R.E., Whitfield M.F., Petrie-Thomas J., Synnes A.R., Cepeda I.L., Keidar A., Rogers M., MacKay M., Hubber-Richard P., Johannesen D. Neonatal Pain, Parenting Stress and Interaction, in Relation to Cognitive and Motor Development at 8 and 18 Months in Preterm Infants. Pain. 2009;143:138–146. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2009.02.014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

