Insights into the Technological Evolution and Research Trends of Mobile Health: Bibliometric Analysis
- PMID: 40218038
- PMCID: PMC11988424
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare13070740
Insights into the Technological Evolution and Research Trends of Mobile Health: Bibliometric Analysis
Abstract
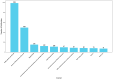
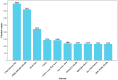
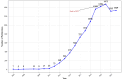
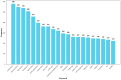
Background/Objectives: Smartphones, with their widespread popularity and diverse apps, have become essential in our daily lives, and ongoing advancements in information technology have unlocked their significant potential in healthcare. Our goal is to identify the future research directions of mobile health (mHealth) by examining its research trends and emerging hotspots. Methods: This study collected mHealth-related literature published between 2005 and 2024 from the Web of Science database. We conducted a descriptive statistic of the annual publication count and categorized the data by authors and institutions. In addition, we developed visualization maps to display the frequency of keyword co-occurrences. Furthermore, overlay visualizations were created to showcase the average publication year of specific keywords, helping to track the changing trends in mHealth research over time. Results: Between 2005 and 2024, a total of 6093 research papers related to mHealth were published. The data have revealed a rapid increase in the number of publications since 2011. However, it was found that research on mHealth has reached a saturation point since 2021. The University of California was the dominant force in mHealth research, with 248 articles. The University of California, the University of London, Harvard University, and Duke University are actively collaborating, which shows a geographical pattern of collaboration. From the analysis of keyword co-occurrence and timeline, the research focus has gradually shifted from solely mHealth technologies to exploring how new technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) in mobile apps, can actively intervene in patient conditions, including breast cancer, diabetes, and other chronic diseases. Privacy protection policies and transparency mechanisms have emerged as an active research focus in current mHealth development. Notably, cutting-edge technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain, and virtual reality (VR) are being increasingly integrated into mHealth systems. These technological convergences are likely to constitute key research priorities in the field, particularly in addressing security vulnerabilities while enhancing service scalability. Conclusions: Although the volume of core research in mobile health (mHealth) is gradually declining, its practical applications continue to expand across diverse domains, increasingly integrating with multiple emerging technologies. It is believed that mobile health still holds enormous potential.
Keywords: bibliometric analysis; data visualization; digital intervention; mHealth app; mental health; mobile health (mHealth).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Exploring the Shift in International Trends in Mobile Health Research From 2000 to 2020: Bibliometric Analysis.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2021 Sep 8;9(9):e31097. doi: 10.2196/31097. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2021. PMID: 34494968 Free PMC article.
-
Visualizing Collaboration Characteristics and Topic Burst on International Mobile Health Research: Bibliometric Analysis.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2018 Jun 5;6(6):e135. doi: 10.2196/mhealth.9581. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2018. PMID: 29871851 Free PMC article.
-
Theme Trends and Knowledge Structure on Mobile Health Apps: Bibliometric Analysis.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020 Jul 27;8(7):e18212. doi: 10.2196/18212. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020. PMID: 32716312 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of mHealth research: mapping the relationship between mobile apps technology and healthcare during COVID-19 outbreak.Global Health. 2022 Jun 28;18(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s12992-022-00856-y. Global Health. 2022. PMID: 35765078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Digital Health Behavior Change Technology: Bibliometric and Scoping Review of Two Decades of Research.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2019 Dec 13;7(12):e13311. doi: 10.2196/13311. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2019. PMID: 31833836 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Integrative technologies in nursing-led interventions for diabetes management: a systematic review of efficacy and outcomes.BMC Nurs. 2025 Jul 4;24(1):846. doi: 10.1186/s12912-025-03435-9. BMC Nurs. 2025. PMID: 40616149 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of a Single Virtual Reality Relaxation Session on Mental-Health Outcomes in Frontline Workers on Duty During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Preliminary Study.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Jun 16;13(12):1434. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13121434. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40565461 Free PMC article.
-
mHealth Applications for Childhood Anxiety Disorders: Current Landscape, Challenges, and Future Directions.Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2025 Jul;27(7):429-440. doi: 10.1007/s11920-025-01613-9. Epub 2025 May 9. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2025. PMID: 40343659 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Istepanian R.S.H., Laxminarayan S., Pattichis C.S. M-Health: Emerging Mobile Health Systems. Springer; New York, NY, USA: 2006.
-
- Feng D.D. Biomedical Information Technology. 1st ed. Academic Press; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2008.
-
- Jat A.S., Gronli T.-M., Ghinea G. Navigating Design Science Research in mHealth Applications: A Guide to Best Practices. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2024;71:14472–14484. doi: 10.1109/TEM.2024.3450178. - DOI
-
- Xu H., Huang S., Qiu C., Liu S., Deng J., Jiao B., Tan X., Ai L., Xiao Y., Belliato M., et al. Monitoring and Management of Home-Quarantined Patients With COVID-19 Using a WeChat-Based Telemedicine System: Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020;22:e19514. doi: 10.2196/19514. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

