Pneumocystis Jirovecii Pneumonia: The Potential of KEX1, MSG1, and MSG2 as Key Antigens in Cytokine Release Assays
- PMID: 40218143
- PMCID: PMC11989143
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15070793
Pneumocystis Jirovecii Pneumonia: The Potential of KEX1, MSG1, and MSG2 as Key Antigens in Cytokine Release Assays
Abstract
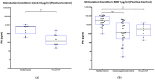
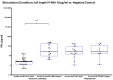
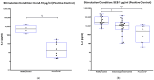
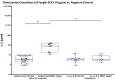
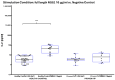
Background/Objectives:Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PJP) is the most frequently diagnosed AIDS-defining illness in Europe, with especially high mortality in HIV-negative patients caused by delayed diagnosis and low awareness. This study aims to evaluate cytokine release assays (CRA) to facilitate a less invasive and resource-efficient PJP specific diagnostic test. We focus on the P. jirovecii antigens Kexin 1 (KEX1), MSG1, and MSG2, which were identified in prior studies as immunologically relevant. Methods: Whole blood samples from 50 participants-22 healthy individuals and 28 immunocompromised individuals, including 8 with proven PJP-were stimulated in vitro with full-length and partial KEX1, MSG1, MSG2, and a combination of all three antigens (PJ-MIX). Following 24 h incubation at 37 °C, cytokine levels of IL-2, IFN-γ, IL-17A, and IL-17F were measured. Results: Stimulation with full-length KEX1, MSG1, MSG2, and PJ-MIX antigens induced higher IL-2 concentrations in the healthy control group compared to the groups IL-2 baseline levels and to the group of proven PJP cases. Similarly, stimulation with full-length KEX1, MSG1, and PJ-MIX elevated IFN-γ levels in the healthy control group compared to baseline IFN-γ levels. Conclusions: Our findings highlight the potential of IL-2 and IFN-γ release following stimulation with PJ antigens, with PJ-MIX eliciting the strongest and most significant responses, suggesting a cumulative antigen effect. This pilot study establishes a foundation for a PJP-specific CRA, deepening our knowledge of T-cell immunity against PJP. Clinically, such a test could, among other applications, evaluate at-risk patients who should receive prophylaxis and may consequently reduce PJP-related morbidity and mortality.
Keywords: IL-17A; IL-17F; Kexin 1; MSG1; MSG2; interferon-γ release assay; interleukin-2 release assay; pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Victor Herbst and Dorinja Zapf were employed by the company EUROIMMUN Medizinische Labordiagnostika AG. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Schmatz D.M., Romancheck M.A., Pittarelli L.A., Schwartz R.E., Fromtling R.A., Nollstadt K.H., Vanmiddlesworth F.L., Wilson K.E., Turner M.J. Treatment of Pneumocystis Carinii Pneumonia with 1,3-Beta-Glucan Synthesis Inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1990;87:5950–5954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5950. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ruhnke M., Cornely O.A., Schmidt-Hieber M., Alakel N., Boell B., Buchheidt D., Christopeit M., Hasenkamp J., Heinz W.J., Hentrich M., et al. Treatment of Invasive Fungal Diseases in Cancer Patients—Revised 2019 Recommendations of the Infectious Diseases Working Party (AGIHO) of the German Society of Hematology and Oncology (DGHO) Mycoses. 2020;63:653–682. doi: 10.1111/myc.13082. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

