The Impact of Quality of Life on Cardiac Arrhythmias: A Clinical, Demographic, and AI-Assisted Statistical Investigation
- PMID: 40218205
- PMCID: PMC11988298
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15070856
The Impact of Quality of Life on Cardiac Arrhythmias: A Clinical, Demographic, and AI-Assisted Statistical Investigation
Abstract
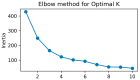
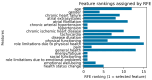
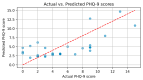
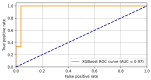
Background/Objectives: Cardiac arrhythmias impact quality of life (QoL) and are often linked to psychological distress. This study examines the relationship between QoL, depression, and arrhythmias using AI-assisted analysis to enhance patient management. Methods: A total of 145 patients with arrhythmias were assessed using an SF-36 health survey (QoL) and a PHQ-9 questionnaire (depression). Statistical analyses included regression, clustering, and AI-based models such as K-means and logistic regression to identify risk factors and patient subgroups. Results: Patients with comorbidities had lower QoL and higher depression scores. PHQ-9 scores negatively correlated with SF-36 mental health components. AI-assisted clustering identified distinct patient subgroups, with older individuals and those with longer disease duration exhibiting the lowest QoL. Logistic regression predicted depression with 93% accuracy, and XGBoost achieved an AUC of 0.97. Conclusions: QoL plays a key role in arrhythmia management, with depression significantly influencing outcomes. AI-driven predictive models offer personalized interventions, improving early detection and treatment. Future research should integrate wearable technology and AI-based monitoring to optimize patient care.
Keywords: PHQ-9; SF-36; artificial intelligence; cardiac arrhythmias; depression; quality of life; statistical methods.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

