Optical Coherence Tomography in Retinal Detachment: Prognostic Biomarkers, Surgical Planning, and Postoperative Monitoring
- PMID: 40218221
- PMCID: PMC11988441
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15070871
Optical Coherence Tomography in Retinal Detachment: Prognostic Biomarkers, Surgical Planning, and Postoperative Monitoring
Abstract
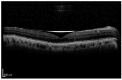
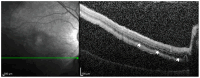
Retinal detachment (RD) is a vision-threatening ocular emergency that necessitates rapid diagnosis and intervention. This review examines the evolving role of optical coherence tomography (OCT) in RD by synthesizing the literature on preoperative biomarkers and advanced image modalities that inform diagnosis, prognosis, and surgical planning. We evaluated studies employing spectral-domain OCT, swept-source OCT, OCT angiography, adaptive optics OCT, and en face OCT to assess photoreceptor integrity, retinal detachment height, intraretinal cystic cavities, outer retinal corrugations and undulation, and macular involvement. The incorporation of OCT assessment into clinical practice may facilitate more precise surgical timing, technique selection, and postoperative monitoring. Further research is needed to standardize imaging protocols and validate specific prognostic biomarkers for optimal surgical outcomes. Key aspects include uniform imaging protocols, validating OCT-derived biomarkers such as ellipsoid zone integrity, and correlating OCT metrics with functional outcomes.
Keywords: OCT angiography; adaptive optics OCT; en face OCT; optical coherence tomography; photoreceptor integrity; prognostic biomarkers; retinal detachment; surgical planning; swept-source OCT.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous