The Prognostic Value of Transcutaneous Oxygen Pressure (TcPO2) in Diabetic Foot Ulcer Healing: A Protocol for a Systematic Review
- PMID: 40218259
- PMCID: PMC11988992
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15070909
The Prognostic Value of Transcutaneous Oxygen Pressure (TcPO2) in Diabetic Foot Ulcer Healing: A Protocol for a Systematic Review
Abstract
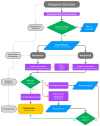
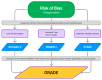
Background/Objectives: Due to poor perfusion, diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) create hypoxic environments, and their chronicity represents a negative factor in wound healing. Transcutaneous oxygen pressure (TcPO2) is a non-invasive method that provides information on oxygen supply to microvascular circulation, useful for determining the severity and progression of peripheral arterial disease (PAD) as well as potentially predicting DFU healing. However, the current literature does not provide strong support for the use of TcPO2 as an independent predictive tool. Methods: This protocol aims to systematically review the available evidence according to PRISMA (2020) guidelines, registered with the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (registration number: CRD42024505907). The following databases will be used: Cochrane Library, EMBASE, Ovid Medline, PubMed, and Web of Science. Additionally, a manual search will be conducted through the references of the included articles. Results: The systematic review will summarize the current evidence on the prognostic value of TcPO2 in DFU healing, identifying gaps in knowledge and potential areas for future research. Conclusions: The findings of this study may clarify the prognostic value of TcPO2 in DFU healing, which could ultimately facilitate clinical management, decision-making, patient care, and potentially reduce treatment costs.
Keywords: blood gas monitoring; diabetic foot; foot ulcer; prognosis; transcutaneous.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Performance of non-invasive bedside vascular testing in the prediction of wound healing or amputation among people with foot ulcers in diabetes: A systematic review.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2024 Mar;40(3):e3701. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3701. Epub 2023 Jul 26. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2024. PMID: 37493206
-
Transcutaneous oxygen pressure as a predictor for short-term survival in patients with type 2 diabetes and foot ulcers: a comparison with ankle-brachial index and toe blood pressure.Acta Diabetol. 2018 Aug;55(8):781-788. doi: 10.1007/s00592-018-1145-8. Epub 2018 Apr 30. Acta Diabetol. 2018. PMID: 29707757 Free PMC article.
-
Photo-Optical Transcutaneous Oxygen Tension Measurement Is of Added Value to Predict Diabetic Foot Ulcer Healing: An Observational Study.J Clin Med. 2020 Oct 14;9(10):3291. doi: 10.3390/jcm9103291. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 33066355 Free PMC article.
-
Transcutaneous oxygen pressure measurement in diabetic foot ulcers: mean values and cut-point for wound healing.J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs. 2013 Nov-Dec;40(6):585-9. doi: 10.1097/WON.0b013e3182a9a7bf. J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs. 2013. PMID: 24202221
-
Toe Pressure in Predicting Diabetic Foot Ulcer Healing: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Ann Vasc Surg. 2019 Oct;60:371-378. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2019.04.011. Epub 2019 Jun 18. Ann Vasc Surg. 2019. PMID: 31220591
References
-
- Magliano D., Boyko E. IDF Diabetes Atlas. International Diabetes Federation; Brussels, Belgium: 2021.
-
- Saeedi P., Petersohn I., Salpea P., Malanda B., Karuranga S., Unwin N., Colagiuri S., Guariguata L., Motala A.A., Ogurtsova K., et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019;157:107843. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

