Effect of Supplemental Essential Oils Blend on Broiler Meat Quality, Fatty Acid Profile, and Lipid Quality
- PMID: 40218323
- PMCID: PMC11987973
- DOI: 10.3390/ani15070929
Effect of Supplemental Essential Oils Blend on Broiler Meat Quality, Fatty Acid Profile, and Lipid Quality
Abstract
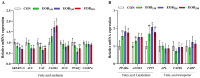
This investigation evaluates the impact of the EOB on chicken growth performance, meat quality, and lipid metabolism. Two hundred and fifty-six one-day-old, white-feathered broilers were randomly allocated to four groups. Each group was subdivided into eight replicates, each with eight unsexed chicks, including the control group (CON), EOB150, EOB250, and EOB350, with 0, 150, 250, and 350 mg/L of the EOB added to the drinking water, respectively. The expression levels of genes associated with antioxidants and lipid metabolism were analyzed using real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Additionally, the FA profile of the breast muscle was determined using gas chromatography. The data displayed that those birds in the EOB250 group had a higher breast muscle index compared to the CON group. The breast meat in the EOB groups showed that there is increased yellowness, water holding capacity (WHC), and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), while cooking losses, drip losses, and saturated fatty acids (SFAs) were reduced compared to the CON. The application of supplements for the EOB250 and EOB350 groups increased antioxidant indices as well as the expression of antioxidant-related genes in the liver and muscles. However, these groups decreased the concentrations of triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), and low-density lipoprotein (LDL-C) in serum and liver compared to the EOB150 and CON groups. These EOB groups downregulated expression of some genes linked to liver FA synthesis and elevated the expressions of lipid β-oxidation-related genes compared to the CON. It can be concluded that the supplementation with 250 mg/L of the EOB has the potential as an alternative water additive in the broiler industry.
Keywords: essential oils; gene expression; growth performance; lipid metabolism; meat quality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Castro F.L.S., Chai L., Arango J., Owens C.M., Smith P.A., Reichelt S., DuBois C., Menconi A. Poultry Industry Paradigms: Connecting the Dots. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2023;32:100310. doi: 10.1016/j.japr.2022.100310. - DOI
-
- Kamal M., Aljahdali N., Jaber F.A., Majrashi K.A., Kishk W.H., Khalil H.A., Abdel-Khalek A.M., Ayoub M.A., Abd El-Hack M.E. Influence of Dietary Chitosan Supplementation on Ovarian Development and Reproductive Performance of New Zealand White Rabbit Does. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2023;23:757–764. doi: 10.2478/aoas-2023-0014. - DOI
-
- Abd El-Hack M.E., Ashour E.A., Aljahdali N., Zabermawi N.M., Baset S.A., Kamal M., Radhi K.S., Moustafa M., Algopishi U., Alshaharni M.O., et al. Does the Dietary Supplementation of Organic Nano-Zinc as a Growth Promoter Impact Broiler’s Growth, Carcass and Meat Quality Traits, Blood Metabolites and Cecal Microbiota? Poult. Sci. 2024;103:103550. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.103550. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Miscellaneous
