Molecular Identification and Expression Analysis of NOD1/2 and TBK1 in Response to Viral or Bacterial Infection in the Spotted Knifejaw (Oplegnathus punctatus)
- PMID: 40218399
- PMCID: PMC11987823
- DOI: 10.3390/ani15071006
Molecular Identification and Expression Analysis of NOD1/2 and TBK1 in Response to Viral or Bacterial Infection in the Spotted Knifejaw (Oplegnathus punctatus)
Abstract
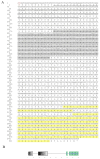
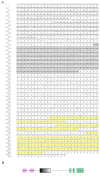
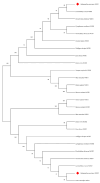
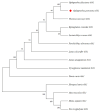
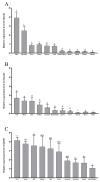
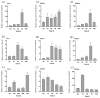
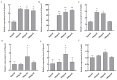
This study investigates the role of the Opnod1, Opnod2, and Optbk1 genes in antiviral and antibacterial immunity of spotted knifejaw (Oplegnathus punctatus). The expression patterns of these genes were analyzed using qRT-PCR in different tissues and at different time points. The open reading frame (ORF) of the Opnod1 gene was 2757 bp in length and encoded 918 amino acids, the ORF of the Opnod2 gene was 2970 bp in length and encoded 990 amino acids, while the Optbk1 gene was 2172 bp in length and encoded 723 amino acids. The Opnod1 and Opnod2 proteins contained three conserved domains (CARD, NOD, and LRR), and Optbk1 contained an STKc domain. The Opnod1, Opnod2, and Optbk1 genes were mainly expressed in immune-related tissues of spotted knifejaw, with the highest relative expression of the Opnod1 in the skin, the Opnod2 in the gill, and the Optbk1 in the liver. The expression of these genes changed significantly in the immune tissues following infection with SKIV-SD and Vibrio harveyi. In kidney cells, the Opnod1, Opnod2, and Optbk1 expression was up-regulated after stimulation by poly I:C and LPS in vitro. The results suggest that the NOD1/2-TBK1 signal pathway may play an important role in the resistance of the spotted knifejaw to virus and bacteria, providing valuable insights for disease-resistant breeding.
Keywords: NOD1; NOD2; Oplegnathus punctatus; TBK1; immunity; infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genome-wide identification, immune response profile and functional characterization of IL-10 from spotted knifejaw (Oplegnathus punctatus) during host defense against bacterial and viral infection.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022 May;124:513-524. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2022.04.026. Epub 2022 Apr 25. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35472402
-
Transcriptomic analysis reveals the gene expression profiles in the spleen of spotted knifejaw (Oplegnathus punctatus) infected by Vibrio harveyi.Dev Comp Immunol. 2022 Aug;133:104432. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2022.104432. Epub 2022 May 6. Dev Comp Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35533850
-
Isolation and identification of a megalocytivirus strain (SKIV-TJ) from cultured spotted knifejaw (Oplegnathus punctatus) in China and its pathogenicity analysis.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023 Oct;141:109034. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2023.109034. Epub 2023 Aug 26. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37640124
-
Three hepcidins from the spotted knifejaw (Oplegnathus punctatus) promote antimicrobial activity via TLR/NFκB pathway.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024 Nov;154:109958. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2024.109958. Epub 2024 Oct 11. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39396559
-
Spotted knifejaw (Oplegnathus punctatus) MyD88: Intracellular localization, signal transduction function and immune responses to bacterial infection.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019 Jun;89:719-726. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2019.04.035. Epub 2019 Apr 14. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30995543
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

