LITES-Based Sensitive CO2 Detection Using 2 μm Diode Laser and Self-Designed 9.5 kHz Quartz Tuning Fork
- PMID: 40218610
- PMCID: PMC11991347
- DOI: 10.3390/s25072099
LITES-Based Sensitive CO2 Detection Using 2 μm Diode Laser and Self-Designed 9.5 kHz Quartz Tuning Fork
Abstract
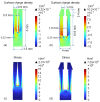
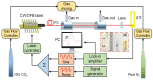
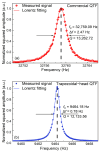
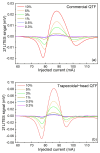
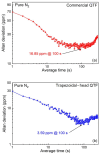
A carbon dioxide (CO2) sensor based on light-induced thermoelastic spectroscopy (LITES) using a 2 μm diode laser and a self-designed low-frequency trapezoidal-head QTF is reported for the first time in this invited paper. The self-designed trapezoidal-head QTF with a low resonant frequency of 9464.18 Hz and a high quality factor (Q) of 12,133.56 can significantly increase the accumulation time and signal level of the CO2-LITES sensor. A continuous-wave (CW) distributed-feedback (DFB) diode laser is used as the light source, and the strongest absorption line of CO2 located at 2004.01 nm is chosen. A comparison between the standard commercial QTF with the resonant frequency of 32.768 kHz and the self-designed trapezoidal-head QTF is performed. The experimental results show that the CO2-LITES sensor with the self-designed trapezoidal-head QTF has an excellent linear response to CO2 concentration, and its minimum detection limit (MDL) can reach 46.08 ppm (parts per million). When the average time is increased to 100 s based on the Allan variance analysis, the MDL of the sensor can be improved to 3.59 ppm. Compared with the 16.85 ppm of the CO2-LITES sensor with the commercial QTF, the performance is improved by 4.7 times, demonstrating the superiority of the self-designed trapezoidal-head QTF.
Keywords: carbon dioxide (CO2); gas sensing; light-induced thermoelastic spectroscopy (LITES); quartz tuning fork.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A Highly Sensitive Light-Induced Thermoelastic Spectroscopy Sensor Using a Charge Amplifier to Improve the Signal-to-Noise Ratio.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Feb 5;25(3):946. doi: 10.3390/s25030946. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39943585 Free PMC article.
-
Ultra-highly sensitive HCl-LITES sensor based on a low-frequency quartz tuning fork and a fiber-coupled multi-pass cell.Photoacoustics. 2022 Jun 17;27:100381. doi: 10.1016/j.pacs.2022.100381. eCollection 2022 Sep. Photoacoustics. 2022. PMID: 36068798 Free PMC article.
-
All-Fiber LITES Sensor Based on Hollow-Core Anti-Resonant Fiber and Self-Designed Low-Frequency Quartz Tuning Fork.Sensors (Basel). 2025 May 6;25(9):2933. doi: 10.3390/s25092933. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40363370 Free PMC article.
-
Highly Sensitive T-Shaped Quartz Tuning Fork Based CH4-Light-Induced Thermoelastic Spectroscopy Sensor with Hydrogen and Helium Enhanced Technique.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Dec 4;24(23):7743. doi: 10.3390/s24237743. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39686280 Free PMC article.
-
Ultra-Highly Sensitive Ammonia Detection Based on Light-Induced Thermoelastic Spectroscopy.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Jul 2;21(13):4548. doi: 10.3390/s21134548. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34283097 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Olabi A.G., Abdelkareem M.A. Renewable energy and climate change. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022;158:112111. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2022.112111. - DOI
-
- Kawamoto R., Mochizuki H., Moriguchi Y., Motohashi M., Sakai Y. Estimation of CO2 emissions of internal combustion engine vehicle and battery electric vehicle using LCA. Sustainability. 2019;11:2690. doi: 10.3390/su11092690. - DOI
-
- Xu H., Ge Y., Zhang C., Wang Z., Xu B., Zhao H., Huang J.B., Wang G., Liu J.X., Feng Y.C., et al. Machine learning reveals the effects of drivers on PM2.5 and CO2 based on ensemble source apportionment method. Atmos. Res. 2023;295:107019. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2023.107019. - DOI
-
- Amato G.D., Chong-Neto H.J., Ortega O.P.M., Ansotegui I., Rosario N., Haahtela T. The effects of climate change on respiratory allergy and asthma induced by pollen and mold allergens. Allergy. 2020;75:2219. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 62335006, 62275065, 62022032, 62405078/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- OEIAM202202/Key Laboratory of Opto-Electronic Information Acquisition and Manipulation (Anhui University), Ministry of Education
- HIT.OCEF.2023011/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
- LBH-Z23144/Heilongjiang Postdoctoral Fund
- LH2024F031/Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

