EEG Signal Prediction for Motor Imagery Classification in Brain-Computer Interfaces
- PMID: 40218770
- PMCID: PMC11991189
- DOI: 10.3390/s25072259
EEG Signal Prediction for Motor Imagery Classification in Brain-Computer Interfaces
Abstract
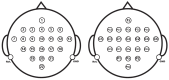
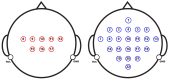
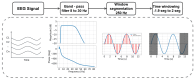
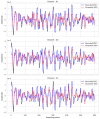
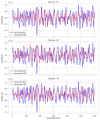
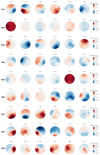
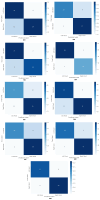
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) based on motor imagery (MI) generally require EEG signals recorded from a large number of electrodes distributed across the cranial surface to achieve accurate MI classification. Not only does this entail long preparation times and high costs, but it also carries the risk of losing valuable information when an electrode is damaged, further limiting its practical applicability. In this study, a signal prediction-based method is proposed to achieve high accuracy in MI classification using EEG signals recorded from only a small number of electrodes. The signal prediction model was constructed using the elastic net regression technique, allowing for the estimation of EEG signals from 22 complete channels based on just 8 centrally located channels. The predicted EEG signals from the complete channels were used for feature extraction and MI classification. The results obtained indicate a notable efficacy of the proposed prediction method, showing an average performance of 78.16% in classification accuracy. The proposed method demonstrated superior performance compared to the traditional approach that used few-channel EEG and also achieved better results than the traditional method based on full-channel EEG. Although accuracy varies among subjects, from 62.30% to an impressive 95.24%, these data indicate the capability of the method to provide accurate estimates from a reduced set of electrodes. This performance highlights its potential to be implemented in practical MI-based BCI applications, thereby mitigating the time and cost constraints associated with systems that require a high density of electrodes.
Keywords: brain–computer interface (BCI); electroencephalography (EEG); motor imagery (MI); multiple regression analysis; regularization analysis; signal prediction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Optimal Channel Selection of Multiclass Motor Imagery Classification Based on Fusion Convolutional Neural Network with Attention Blocks.Sensors (Basel). 2024 May 16;24(10):3168. doi: 10.3390/s24103168. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38794022 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Feature Selection and Classification Techniques to Improve the Performance of an Electroencephalography-Based Motor Imagery Brain-Computer Interface System.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Aug 1;24(15):4989. doi: 10.3390/s24154989. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39124036 Free PMC article.
-
Modified CC-LR algorithm with three diverse feature sets for motor imagery tasks classification in EEG based brain-computer interface.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2014 Mar;113(3):767-80. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2013.12.020. Epub 2014 Jan 3. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2014. PMID: 24440135
-
EEG-Based Brain-Computer Interfaces Using Motor-Imagery: Techniques and Challenges.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Mar 22;19(6):1423. doi: 10.3390/s19061423. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30909489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[A review on electroencephalogram based channel selection].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Apr 25;41(2):398-405. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.202308034. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38686423 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Effect of EEG Electrode Numbers on Source Estimation in Motor Imagery.Brain Sci. 2025 Jun 26;15(7):685. doi: 10.3390/brainsci15070685. Brain Sci. 2025. PMID: 40722278 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhu H.Y., Hieu N.Q., Hoang D.T., Nguyen D.N., Lin C.T. A human-centric metaverse enabled by brain-computer interface: A survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials. 2024;26:2120–2145. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2024.3387124. - DOI
-
- Al-Qaysi Z., Ahmed M., Hammash N.M., Hussein A.F., Albahri A., Suzani M., Al-Bander B., Shuwandy M.L., Salih M.M. Systematic review of training environments with motor imagery brain–computer interface: Coherent taxonomy, open issues and recommendation pathway solution. Health Technol. 2021;11:783–801. doi: 10.1007/s12553-021-00560-8. - DOI
-
- Amin S.U., Altaheri H., Muhammad G., Alsulaiman M., Abdul W. Attention based Inception model for robust EEG motor imagery classification; Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC); Glasgow, UK. 17–20 May 2021; pp. 1–6.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

