ECG Sensor Design Assessment with Variational Autoencoder-Based Digital Watermarking
- PMID: 40218832
- PMCID: PMC11991367
- DOI: 10.3390/s25072321
ECG Sensor Design Assessment with Variational Autoencoder-Based Digital Watermarking
Abstract
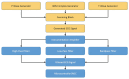
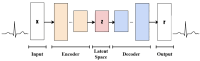
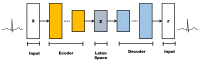
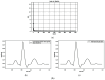
Designing an ECG sensor circuit requires a comprehensive approach to detect, amplify, filter, and condition the weak electrical signals produced by the heart. To evaluate sensor performance under realistic conditions, diverse ECG signals with embedded watermarks are generated, enabling an assessment of how effectively the sensor and its signal-conditioning circuitry handle these modified signals. A Variational Autoencoder (VAE) framework is employed to generate the watermarked ECG signals, addressing critical concerns in the digital era, such as data security, authenticity, and copyright protection. Three watermarking strategies are examined in this study: embedding watermarks in the mean (μ) of the VAE's latent space, embedding them through the latent variable (z), and using post-reconstruction watermarking in the frequency domain. Experimental results demonstrate that watermarking applied through the mean (μ) and in the frequency domain achieves a low Mean Squared Error (MSE) while maintaining stable signal fidelity across varying watermark strengths (α), latent space dimensions, and noise levels. These findings indicate that the mean (μ) and frequency domain methods offer robust performance and are minimally affected by changes in these parameters, making them particularly suitable for preserving ECG signal quality. By contrasting these methods, this study provides insights into selecting the most appropriate watermarking technique for ECG sensor applications. Incorporating watermarking into sensor design not only strengthens data security and authenticity but also supports reliable signal acquisition in modern healthcare environments. Overall, the results underscore the effectiveness of combining VAEs with watermarking strategies to produce high-fidelity, resilient ECG signals for both sensor performance evaluation and the protection of digital content.
Keywords: Fourier-simulated ECG dataset; latent variable space; variational AutoEncoder; watermarking technology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures











Similar articles
-
Ecg signal watermarking using QR decomposition.Phys Eng Sci Med. 2024 Dec;47(4):1677-1690. doi: 10.1007/s13246-024-01480-3. Epub 2024 Sep 12. Phys Eng Sci Med. 2024. PMID: 39266907
-
Hiding patients confidential datainthe ECG signal viaa transform-domain quantization scheme.J Med Syst. 2014 Jun;38(6):54. doi: 10.1007/s10916-014-0054-9. Epub 2014 May 17. J Med Syst. 2014. PMID: 24832688
-
A denoising method for ECG signals based on CEEMDAN-TSO and stacked sparse autoencoders.Comput Biol Med. 2025 Apr;188:109818. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2025.109818. Epub 2025 Feb 20. Comput Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 39983358
-
Optimizing Wavelet ECG Watermarking to Maintain Measurement Performance According to Industrial Standard.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Oct 11;18(10):3401. doi: 10.3390/s18103401. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30314291 Free PMC article.
-
Wavelet transformation based watermarking technique for human electrocardiogram (ECG).J Med Syst. 2005 Dec;29(6):589-94. doi: 10.1007/s10916-005-6126-0. J Med Syst. 2005. PMID: 16235811
References
-
- Li G., Ma X., Wang X., Yue H., Li J., Liu L., Feng X., Xue J. Optimizing deep neural networks on intelligent edge accelerators via flexible-rate filter pruning. J. Syst. Archit. 2022;124:102431. doi: 10.1016/j.sysarc.2022.102431. - DOI
-
- Liu L., Ma X., Liu H., Li G., Liu L. FlexPDA: A flexible programming framework for deep learning accelerators. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2022;37:1200–1220. doi: 10.1007/s11390-021-1406-9. - DOI
-
- Li G., Ma X., Wang X., Liu L., Xue J., Feng X. Fusion-catalyzed pruning for optimizing deep learning on intelligent edge devices. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2020;39:3614–3626. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2020.3013050. - DOI
-
- Sanivarapu P.V., Rajesh K.N.V.P.S., Reddy N.V.R., Reddy K.V.K., Rao P.V.R., Reddy A.S. Patient Data Hiding into ECG Signal Using Watermarking in Transform Domain. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2020;43:213–226. doi: 10.1007/s13246-019-00838-2. - DOI
-
- Kaur S., Singhal R., Farooq O., Ahuja B.S. Digital Watermarking of ECG Data for Secure Wireless Communication; Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Recent Trends in Information; Kerala, India. 12–13 March 2010; pp. 140–144. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

