Blueberry Extract and Resistance Training Prevent Left Ventricular Redox Dysregulation and Pathological Remodeling in Experimental Severe Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
- PMID: 40218902
- PMCID: PMC11990098
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17071145
Blueberry Extract and Resistance Training Prevent Left Ventricular Redox Dysregulation and Pathological Remodeling in Experimental Severe Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Abstract
Objective: To investigate whether the regular administration of blueberry extract and low-intensity resistance exercise training (RT), either alone or in combination, during the development of monocrotaline (MCT)-induced severe pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) in rats protect the left ventricle (LV) from redox dysregulation and pathological remodeling.
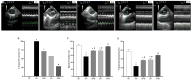
Methods: Groups of seven male Wistar rats were formed for the experiment: sedentary control; sedentary hypertensive; sedentary hypertensive blueberry; exercise hypertensive; and exercise hypertensive blueberry. PAH was experimentally induced through a single intraperitoneal administration of MCT at a dose of 60 mg/kg. One day after injection, the blueberry groups started receiving a daily dose of blueberry extract (100 mg/kg) by gavage, while the exercise groups initiated a three-week program of RT (ladder climbing; 15 climbs carrying 60% of maximum load; one session/day; 5 times/week). Echocardiographic evaluations were conducted 23 days after injection, and the rats were euthanized the next day to harvest LV tissue.
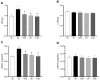
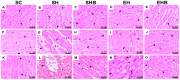
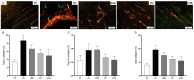
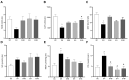
Results: Separately, blueberry extract and RT mitigated augments in pulmonary artery resistance, LV tissue redox dysregulation (i.e., increased PC levels) and detrimental remodeling (i.e., reduced inflammation), and reductions in ejection fraction (EF) and fractional shortening (FS) caused by PAH. The combination of treatments prevented reductions in EF and FS, along with the development of a D-shaped LV.
Conclusions: blueberry extract and moderate-intensity resistance training administered during the development of MCT-induced severe PAH in rats prevented LV redox dysregulation and pathological remodeling, thereby preserving its function.
Keywords: adverse remodeling; blueberry extract; ejection fraction; exercise training; left ventricle; pulmonary artery resistance; redox state.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combined exercise hinders the progression of pulmonary and right heart harmful remodeling in monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2025 Jan 1;138(1):182-194. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00379.2024. Epub 2024 Nov 29. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2025. PMID: 39611819
-
Blueberry extract decreases oxidative stress and improves functional parameters in lungs from rats with pulmonary arterial hypertension.Nutrition. 2020 Feb;70:110579. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2019.110579. Epub 2019 Sep 13. Nutrition. 2020. PMID: 31743815
-
Blueberry extract improves redox balance and functional parameters in the right ventricle from rats with pulmonary arterial hypertension.Eur J Nutr. 2022 Feb;61(1):373-386. doi: 10.1007/s00394-021-02642-9. Epub 2021 Aug 10. Eur J Nutr. 2022. PMID: 34374852
-
Combined physical training protects the left ventricle from structural and functional damages in experimental pulmonary arterial hypertension.Clin Hypertens. 2024 May 1;30(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s40885-024-00270-z. Clin Hypertens. 2024. PMID: 38689333 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance Exercise Training Mitigates Left Ventricular Dysfunctions in Pulmonary Artery Hypertension Model.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2022 Oct;119(4):574-584. doi: 10.36660/abc.20210681. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 36074480 Free PMC article. English, Portuguese.
References
-
- Kishiki K., Singh A., Narang A., Gomberg-Maitland M., Goyal N., Maffessanti F., Besser S.A., Mor-Avi V., Lang R.M., Addetia K. Impact of severe pulmonary arterial hypertension on the left heart and prognostic implications. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2019;32:1128–1137. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2019.05.008. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Redout E.M., Wagner M.J., Zuidwijk M.J., Boer C., Musters R.J., van Hardeveld C., Paulus W., Simonides W.S. Right-ventricular failure is associated with increased mitochondrial complex II activity and production of reactive oxygen species. Cardiovasc. Res. 2007;75:770–781. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2007.05.012. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Souza-Rabbo M.P., Silva L.F., Auzani J.A., Picoral M., Khaper N., Belló-Klein A. Effects of a chronic exercise training protocol on oxidative stress and right ventricular hypertrophy in monocrotaline-treated rats. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2008;35:944–948. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2008.04936.x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

