Nutritional Support of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- PMID: 40218907
- PMCID: PMC11990120
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17071149
Nutritional Support of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Abstract
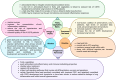
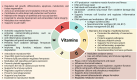
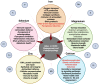
Background: COPD is a heterogenous disease of the respiratory tract caused by diverse genetic factors along with environmental and lifestyle-related effects such as industrial dust inhalation and, most frequently, cigarette smoking. These factors lead to airflow obstruction and chronic respiratory symptoms. Additionally, the increased risk of infections exacerbates airway inflammation in COPD patients. As a consequence of the complex pathomechanisms and difficulty in treatment, COPD is among the leading causes of mortality both in the western countries and in the developing world. Results: The management of COPD is still a challenge for the clinicians; however, alternative interventions such as smoking cessation and lifestyle changes from a sedentary life to moderate physical activity with special attention to the diet may ameliorate patients' health. Here, we reviewed the effects of different dietary components and supplements on the conditions of COPD. Conclusions: COPD patients are continuously exposed to heavy metals, which are commonly present in cigarette smoke and polluted air. Meanwhile, they often experience significant nutrient deficiencies, which affect the detoxification of these toxic metals. This in turn can further disrupt nutritional balance by interfering with the absorption, metabolism, and utilization of essential micronutrients. Therefore, awareness and deliberate efforts should be made to check levels of micronutrients, with special attention to ensuring adequate levels of antioxidants, vitamin D, vitamin K2, magnesium, and iron, as these may be particularly important in reducing the risk of COPD development and limiting disease severity.
Keywords: COPD; inorganic elements; nutrition; vitamins.
Conflict of interest statement
L.G.P. is the CEO of Anthelos Ltd. I.K. is an employee of Avidin Ltd. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Guleria R., Arora S., Kumar G., Mohan A. Does Systemic Inflammation Effects Nutritional Status and Severity of COPD? Obstr. Lung Dis. 2016;150:850A.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2023-1.1.1-PIACI_FÓKUSZ-2024-00036/National Research, Development, and Innovation Office (NKFI), Hungary
- 2020-1.1.6-JÖVŐ-2021-00003/National Research, Development, and Innovation Office (NKFI), Hungary
- 2022-1.2.6-TÉT-IPARI-TR-2022-00023/National Research, Development, and Innovation Office (NKFI), Hungary
- 142877 FK22/National Research, Development, and Innovation Office (NKFI), Hungary.
- BO/00582/22/8/János Bolyai Research Scholarship of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

