Rural Health: Low Obesity Rates Among Students in Portugal's Countryside
- PMID: 40218911
- PMCID: PMC11990436
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17071153
Rural Health: Low Obesity Rates Among Students in Portugal's Countryside
Abstract
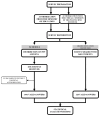
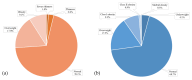
Dietary habits significantly influence students' health status, with overweight and obesity posing serious global challenges linked to chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular conditions. Our cross-sectional study assessed overweight and obesity prevalence among students in Guarda, Portugal, analyzing the nutritional and lifestyle habits of 2083 students aged 6 to 58 years. The sample included 1762 school children and 321 higher education adults, grouped into age intervals: 5-12, 13-19, 20-39, and 40-59 years. BMI analysis revealed obesity rates of 9.1% in children and 9.7% in adults, with younger children, particularly males, showing higher rates compared to older children. Increased physical activity and reduced sedentary time were correlated with a lower BMI. The observed obesity rates suggest that factors such as physical activity levels, traditional dietary patterns, and access to fresh foods in this region of Portugal may contribute to better health outcomes among students.
Keywords: Body Mass Index; eating behaviours; physical activity; student health status.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Jacob C.M., Hardy-Johnson P.L., Inskip H.M., Morris T., Parsons C.M., Barrett M., Hanson M., Woods-Townsend K., Baird J. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of School-Based Interventions with Health Education to Reduce Body Mass Index in Adolescents Aged 10 to 19 Years. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2021;18:1. - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization Obesity and Overweight. [(accessed on 23 July 2024)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

