A 12-Week, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Lactobacillus plantarum LMT1-48 on Body Fat Loss
- PMID: 40218949
- PMCID: PMC11990557
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17071191
A 12-Week, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Lactobacillus plantarum LMT1-48 on Body Fat Loss
Abstract
Objectives: This study aims to evaluate the efficacy and safety of probiotics for body fat reduction in obese individuals.
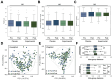
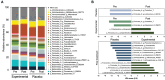
Methods: A total of 106 participants with a body mass index between 25 and 30 kg/m2 were randomly assigned to either the experimental group treating with Lactobacillus plantarum LMT1-48 or the placebo group in the placebo-controlled clinical trial. Body composition was assessed by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and computed tomography. Fecal samples between the groups were contrasted via DNA sequencing for evaluation of the microbiota and its diversity.
Results: After 12 weeks of follow-up period, the body fat mass decreased significantly, from 30.0 ± 4.4 to 28.3 ± 4.1 kg in the experimental group (p = 0.009). The percentage of body fat in the two groups showed a similar trend (p = 0.004).
Conclusions: LMT1-48 also positively influenced the microbial taxa linked to obesity analyzed by gut microbiome sequencing. LMT1-48 is a safe and collaborative agent to reduce obesity.
Keywords: Lactobacillus plantarum; body fat loss; obesity; probiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
J.Y. and D.-w.R. are employees of Medytox Inc., Suwon, Republic of Korea. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted without any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Jakubiec J., Gmitrzuk J., Malinka Z., Wiśniewska K., Jachymek A., Opatowska M., Kucharski T., Karasiński M. Obesity in Adults: Causes, Health Consequences, and Treatment Methods. Qual. Sport. 2024;17:53051.
-
- Sekar P.K.C., Veerabathiran R. Genes linked to obesity-related infertility: Bridging the knowledge gap. Reprod. Dev. Med. 2024;8:121–129. doi: 10.1097/RD9.0000000000000096. - DOI
-
- Veerabathiran R., Sivakumar S., Kalarani I.B., Mohammed V. A review of genes associated with obesity susceptibility: Findings from association studies. J. Health Sci. Med. Res. 2023;41:2023959. doi: 10.31584/jhsmr.2023959. - DOI
-
- Kim D.H., Yang B.S. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Link of Obesity to Chronic Diseases. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2006;15:121–128.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

