Prevalence of Obesity Among Elementary School Children in Cyprus: The National COSI Program
- PMID: 40218972
- PMCID: PMC11990531
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17071213
Prevalence of Obesity Among Elementary School Children in Cyprus: The National COSI Program
Abstract
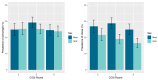
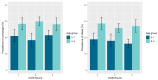
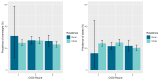
Background/Objectives: A worldwide epidemic of overweight and obesity is an ongoing global health concern. This rise in overweight and obesity among children contributes to the increasing pattern of current and future physiological and psychological problems. Our study aimed at examining overweight and obesity among elementary school children in Cyprus. Methods: Data on children's age, sex, place of residence (urban/rural) and weight/height status were collected using the WHO Childhood Obesity Surveillance Initiative (COSI) in Cyprus, using standardized measurements of children aged 6-9 years enrolled in the first and fourth class of elementary schools during the academic year 2021-2022. We describe the prevalence and distribution of overweight and obesity, while we also compare the findings with previous rounds of the COSI program. Results: A total of 1662 children were evaluated (830 boys and 832 girls, 952 from the first and 710 from the fourth class, and 1303 from urban and 369 from rural areas). The study showed 335 children with overweight (20.1%) and 275 with obesity (16.5%). Both overweight [158 (22.2%, 95% CI: 19.2-25.5%)] and obesity [149 (21.0%, 95% CI: 18.1-24.2%)] was significantly higher in children aged 8-9 years of age compared to younger children (6-7 years) (p < 0.0001) and was also higher in boys compared to girls (p = 0.0007). No difference was seen by place of residence or round of examination. Conclusions: Our study confirmed that both overweight and obesity remain at high levels over the past decade in both boys and girls in Cyprus.
Keywords: Cyprus; children; epidemiology; obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128.9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet. 2017;390:2627–2642. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32129-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- McManus K., Temples H. Obesity in adolescents: Prevention and treatment to change their future. J. Nurse Pract. 2021;17:972–978. doi: 10.1016/j.nurpra.2021.04.018. - DOI
-
- Buoncristiano M., Spinelli A., Williams J., Nardone P., Rito A.I., García-Solano M., Grøholt E.K., Gutiérrez-González E., Klepp K.I., Starc G., et al. Childhood overweight and obesity in Europe: Changes from 2007 to 2017. Obes. Rev. 2021;22((Suppl. S6)):e13226. doi: 10.1111/obr.13226. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

