Investigating the Therapeutic Potential of the Ketogenic Diet in Modulating Neurodegenerative Pathophysiology: An Interdisciplinary Approach
- PMID: 40219025
- PMCID: PMC11990313
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17071268
Investigating the Therapeutic Potential of the Ketogenic Diet in Modulating Neurodegenerative Pathophysiology: An Interdisciplinary Approach
Abstract
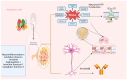
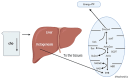
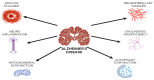
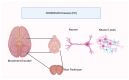
The ketogenic diet (KD) is a dietary intervention comprising a high-fat, low-carbohydrate, and moderate-protein intake designed to induce a metabolic state known as ketosis, whereby ketone bodies are produced as an alternative source of energy. Initially established as a treatment for intractable epilepsy, the KD has subsequently gained significant attention for its potential to manage neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and Huntington's disease. Ketone bodies, such as beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB), have been demonstrated to possess neuroprotective properties. The increasing prevalence of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and Huntington's disease, poses a significant public health challenge worldwide. With neurological disorders being the second-leading cause of death globally, the need for effective therapeutic interventions has never been more urgent. Recent evidence suggests that dietary interventions, particularly the ketogenic diet, offer promising potential in mitigating the progression of these diseases by influencing metabolic processes and providing neuroprotective benefits. The ketogenic diet, characterized by high-fat and low-carbohydrate intake, induces ketosis, leading to the production of ketone bodies like beta-hydroxybutyrate, which enhance mitochondrial efficiency, reduce oxidative stress, and modulate inflammatory pathways-mechanisms critical in neurodegenerative pathophysiology. This review explores the role of the ketogenic diet in managing neurological conditions, examining its mechanisms of action, historical context, and therapeutic efficacy. The paper also discusses emerging evidence linking the ketogenic diet to improved cognitive function, reduced motor symptoms, and enhanced mitochondrial activity in patients with neurodegenerative disorders. Additionally, the review highlights the need for further research to refine the therapeutic applications of the ketogenic diet, investigate its impact on various neurodegenerative diseases, and better understand its potential long-term effects. This study underscores the importance of nutrition as a vital aspect of the treatment strategy for neurological diseases, advocating for continued exploration of dietary interventions to improve brain health and function.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Parkinson’s disease; beta-hydroxybutyrate; cognitive function; ketogenic diet; mitochondrial function; neurodegenerative diseases; neuroprotection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this review paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ketogenic Diet: A Promising Neuroprotective Composition for Managing Alzheimer's Diseases and its Pathological Mechanisms.Curr Mol Med. 2022;22(7):640-656. doi: 10.2174/1566524021666211004104703. Curr Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 34607541 Review.
-
Beneficial Effects of Exogenous Ketogenic Supplements on Aging Processes and Age-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases.Nutrients. 2021 Jun 26;13(7):2197. doi: 10.3390/nu13072197. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34206738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Ketogenic Diet and Alzheimer's Disease.J Nutr Health Aging. 2022;26(6):606-614. doi: 10.1007/s12603-022-1807-7. J Nutr Health Aging. 2022. PMID: 35718870 Review.
-
Activation of G protein-coupled receptors by ketone bodies: Clinical implication of the ketogenic diet in metabolic disorders.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Oct 20;13:972890. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.972890. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36339405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Neuroprotection by Ketone Bodies and Ketogenic Diet in Cerebral Ischemia and Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 21;25(1):124. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010124. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203294 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
3-Hydroxybutyrate, a metabolite in sustaining neuronal cell vitality: a mendelian randomization and in vitro experimentation.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2025 Jul 11;22(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s12986-025-00960-x. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40646620 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kawka J., Baranowska A., Baranowska K., Czyżewski F., Filipek K., Muciek M., Mrugała S., Mrugała W., Skierkowski B., Zalewska N. The impact of eating disorders on glaucoma. J. Educ. Health Sport. 2024;66:49959.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

