Bridging Molecular Insights and Agronomic Innovations: Cutting-Edge Strategies for Overcoming Boron Deficiency in Sustainable Rapeseed Cultivation
- PMID: 40219062
- PMCID: PMC11990839
- DOI: 10.3390/plants14070995
Bridging Molecular Insights and Agronomic Innovations: Cutting-Edge Strategies for Overcoming Boron Deficiency in Sustainable Rapeseed Cultivation
Abstract
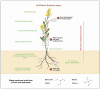
Boron (B) is an essential micronutrient for the growth, development, and maintenance of cellular integrity in vascular plants, and is especially important in cell wall synthesis and reproductive development. Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.), one of the dominant oil crops globally, has a high boron demand and its yield is dramatically decreased under B-deficiency conditions. Rapeseed, which is very sensitive to boron deficiency, suffers from reduced growth and reproductive development, ultimately causing severe yield losses. Here, we reviewed the present state of knowledge on the physiological function of boron in rapeseed, mechanisms of boron uptake and transport, specific effects of boron deficiency in rapeseed, and approaches to alleviate boron deficiency in rapeseed at the agronomical and molecular levels. A specific focus is given to recent molecular breakthroughs and agronomic approaches that may improve boron efficiency. The review focuses on practices that may alleviate the problems caused by boron-deficient soils by investigating the genetic and physiological mechanisms of boron tolerance. In summary, this review describes the integration of molecular information with practical agronomy as an important aspect of breeding future nutrient-efficient rapeseed cultivars that can sustain increasing yields while being cultivated in regions with boron-deficient soils.
Keywords: BORs; NIPs; boron; rapeseed; transporters.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of Rapeseed (Brassica napus) Cultivars With a High Tolerance to Boron-Deficient Conditions.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Aug 7;9:1142. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01142. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 30131820 Free PMC article.
-
Genotypic differences in the synergistic effect of nitrogen and boron on the seed yield and nitrogen use efficiency of Brassica napus.J Sci Food Agric. 2022 Jul;102(9):3563-3571. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.11700. Epub 2021 Dec 13. J Sci Food Agric. 2022. PMID: 34854085
-
BnaA4.BOR2 contributes the tolerance of rapeseed to boron deficiency by improving the transport of boron from root to shoot.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2024 Mar;208:108508. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2024.108508. Epub 2024 Mar 7. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38490152
-
Research progress and mitigation strategies for pod shattering resistance in rapeseed.PeerJ. 2024 Oct 17;12:e18105. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18105. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39430553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Boron deficiency in woody plants: various responses and tolerance mechanisms.Front Plant Sci. 2015 Oct 27;6:916. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00916. eCollection 2015. Front Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 26579163 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- O’Neill M.A., Ishii T., Albersheim P., Darvill A.G. Rhamnogalacturonan II: Structure and function of a borate cross-linked cell wall pectic polysaccharide. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2004;55:109–139. - PubMed
-
- Camacho-Cristóbal J.J., Navarro-Gochicoa M.T., Rexach J., González-Fontes A., Herrera-Rodríguez M.B. Plant Micronutrient Use Efficiency. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2018. Plant response to boron deficiency and boron use efficiency in crop plants; pp. 109–121.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

