Core Mycorrhizal Fungi Promote Seedling Growth in Dendrobium officinale: An Important Medicinal Orchid
- PMID: 40219092
- PMCID: PMC11990756
- DOI: 10.3390/plants14071024
Core Mycorrhizal Fungi Promote Seedling Growth in Dendrobium officinale: An Important Medicinal Orchid
Abstract
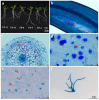
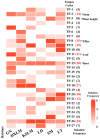
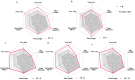
The critically endangered orchid Dendrobium officinale, valued for its medicinal properties, depends on specific seedling-associated mycorrhizal fungi (SAMF) for successful early-stage seedling development. However, conservation efforts are often hindered by difficulties in obtaining suitable SAMF, leading to poor seedling establishment in both natural and cultivated environments. In this study, we explored the growth-promoting effects of SAMF and evaluated the performances of synthetic fungal combinations. Our results demonstrated that mycorrhizal fungi, widely distributed across multiple habitats with high isolation frequencies, significantly promoted the growth of D. officinale, with specific fungi favoring different growth parameters. Tulasnella sp. TP-2 and TP-3 significantly improved stem diameter and plant height by 2.622 mm and 4.621 cm, while Tulasnella sp. TP-8 significantly increased tillering by a factor of 4.47. Additionally, Tulasnella sp. TP-11 and TP-13 markedly increased the number of new leaves (4.45) and new roots (2.688), respectively, identifying them as essential core OMFs for D. officinale seedlings. Contrary to expectations, synthetic fungal combinations composed of core orchid mycorrhizal fungi (core OMFs) did not exhibit synergistic growth-promoting effects. Instead, pronounced offset effects were observed, indicating that interactions between fungi may introduce competition or inhibition, limiting their collective ability to enhance plant growth. Our results confirmed that the core OMFs significantly promoted the growth of D. officinale seedlings. These core OMFs can serve as essential components in specialized microbial fertilizers for D. officinale, improving growth efficiency and yield, and supporting the sustainable development of the D. officinale industry.
Keywords: growth-promoting fungi; seedling growth; seedling-associated mycorrhizal fungi; synergistic/offset effects; synthetic fungal combinations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Using Ex Situ Seedling Baiting to Capture Seedling-Associated Mycorrhizal Fungi in Medicinal Orchid Dendrobium officinale.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Sep 29;8(10):1036. doi: 10.3390/jof8101036. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36294601 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of different mycobionts on symbiotic germination and seedling growth of Dendrobium officinale, an important medicinal orchid.Bot Stud. 2020 Jan 27;61(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s40529-019-0278-6. Bot Stud. 2020. PMID: 31989371 Free PMC article.
-
What role does the seed coat play during symbiotic seed germination in orchids: an experimental approach with Dendrobium officinale.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Jul 29;22(1):375. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03760-0. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 35906552 Free PMC article.
-
Perspective and challenges of mycorrhizal symbiosis in orchid medicinal plants.Chin Herb Med. 2024 Mar 8;16(2):172-179. doi: 10.1016/j.chmed.2024.03.001. eCollection 2024 Apr. Chin Herb Med. 2024. PMID: 38706832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Orchid Reintroduction Based on Seed Germination-Promoting Mycorrhizal Fungi Derived From Protocorms or Seedlings.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Jun 30;12:701152. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.701152. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34276753 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ecological specificity of fungi on seedling establishment in Dendrobium huoshanense: a narrow distributed medicinal orchid.Mycorrhiza. 2025 Jun 9;35(3):41. doi: 10.1007/s00572-025-01216-5. Mycorrhiza. 2025. PMID: 40488931 No abstract available.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

