Unlocking the Therapeutic Potential of Patchouli Leaves: A Comprehensive Review of Phytochemical and Pharmacological Insights
- PMID: 40219102
- PMCID: PMC11990424
- DOI: 10.3390/plants14071034
Unlocking the Therapeutic Potential of Patchouli Leaves: A Comprehensive Review of Phytochemical and Pharmacological Insights
Abstract
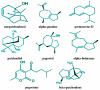
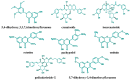
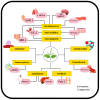
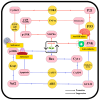
Plant-based products play an increasingly vital role in the pharmaceutical industry, including Pogostemon cablin (Blanco) Benth. (patchouli), which is notable for its rich history and extensive use in traditional medicine. Patchouli has a longstanding historical use as a remedy for a wide range of health conditions, including colds, fevers, headaches, inflammation, digestive disorders, and insect and snake bites. Comprehensive phytochemical studies have revealed that patchouli leaves contain diverse valuable bioactive compounds, notably patchouli alcohol, β-patchoulene, pogostone, α-bulnesene, and β-caryophyllene. Recent studies have demonstrated that patchouli leaves exhibit various pharmacological properties, including anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antidepressant, and anticancer effects. Despite robust traditional knowledge, specific therapeutic applications of patchouli leaves require scientific validation and standardization of their bioactive compounds. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the existing literature on the phytochemical composition, pharmacological properties, and underlying mechanisms of action of patchouli essential oil (PEO) and plant extracts obtained from patchouli leaves. It offers detailed insights into potential therapeutic applications, aiming to inform and guide future research across multiple medical disciplines. Ultimately, this review underscores the need for further research to validate and develop the medicinal applications of patchouli leaves, providing a foundation for future healthcare advancements.
Keywords: medicinal plant; patchouli (Pogostemon cablin); patchouli leaves; pharmacological activities; phytochemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Comprehensive Review on the Phytochemical Constituents and Pharmacological Activities of Pogostemon cablin Benth.: An Aromatic Medicinal Plant of Industrial Importance.Molecules. 2015 May 12;20(5):8521-47. doi: 10.3390/molecules20058521. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 25985355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Review on Pharmacological Activities of Pachypodol: A Bioactive Compound of an Aromatic Medicinal Plant Pogostemon Cablin Benth.Molecules. 2023 Apr 14;28(8):3469. doi: 10.3390/molecules28083469. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37110702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological activities and mechanisms of action of Pogostemon cablin Benth: a review.Chin Med. 2021 Jan 7;16(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s13020-020-00413-y. Chin Med. 2021. PMID: 33413544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Patchouli Essential Oil and Its Derived Compounds Revealed Prebiotic-Like Effects in C57BL/6J Mice.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Oct 17;10:1229. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01229. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31680986 Free PMC article.
-
Fabrication and Evaluation of Polyvinyl Alcohol/Corn Starch/Patchouli Oil Hydrogel Films Loaded with Silver Nanoparticles Biosynthesized in Pogostemon cablin Benth Leaves' Extract.Molecules. 2023 Feb 21;28(5):2020. doi: 10.3390/molecules28052020. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36903266 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yeşilyurt S., Gürgan M., Sertkahya M. Medicinal and Aromatic Plants: Current Research Status, Value-Addition to Their Waste, and Agro-Industrial Potential (Vol I) Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2024. Biologically Active Compounds from Medicinal and Aromatic Plants for Industrial Applications; pp. 1–11. - DOI
-
- Abate L., Bachheti A., Bachheti R.K., Husen A., Getachew M., Pandey D.P. Non-Timber Forest Products. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2021. Potential Role of Forest-Based Plants in Essential Oil Production: An Approach to Cosmetic and Personal Health Care Applications; pp. 1–18. - DOI
-
- Ahad B., Shahri W., Rasool H., Reshi Z.A., Rasool S., Hussain T. Medicinal and Aromatic Plants. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2021. Medicinal Plants and Herbal Drugs: An Overview; pp. 1–40. - DOI
-
- Yan W., Liu X., Cao S., Yu J., Zhang J., Yao G., Yang H., Yang D., Wu Y. Molecular Basis of Pogostemon cablin Responding to Continuous Cropping Obstacles Revealed by Integrated Transcriptomic, MiRNA and Metabolomic Analyses. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023;200:116862. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2023.116862. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

