Transcriptomic miRNA and mRNA signatures in primary prostate cancer that are associated with lymph-node invasion
- PMID: 40219635
- PMCID: PMC11992358
- DOI: 10.1002/ctm2.70288
Transcriptomic miRNA and mRNA signatures in primary prostate cancer that are associated with lymph-node invasion
Abstract
Background: Nomograms or comparable techniques can be used to determine which patients with prostate cancer (PCa) will benefit from extended pelvic lymph node dissection (ePLND). While nomograms help guide clinical decisions, ∼80% of the patients undergo unnecessary ePLND. This pilot study aims to identify both transcriptomic mRNA and microRNA (miR) signatures in primary PCa tumours that are associated with the presence of lymph node metastasis (LNM).
Methods: Primary PCa tumours obtained from 88 patients (pathologically diagnosed as N0 [pN0, n = 44] or as N1 [pN1, n = 44]) were profiled using two different probe-based captured direct assays based on next-generation sequencing and targeting 19398 mRNA transcripts (human transcriptome panel [HTP] dataset) and 2083 miRs (miRs whole-transcriptome assay [WTA] dataset). The TCGA-PRAD (pN0 [n = 382] and pN1 [n = 70]) and GSE220095 (pN0 [n = 138] and pN1 [n = 17]) datasets were used for validation using bioinformatic analyses.
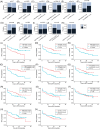
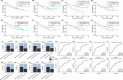
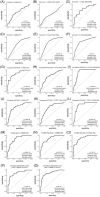
Results: A four-mRNA signature (CHRNA2, NPR3, VGLL3 and PAH) was found in primary tumour tissue samples from pN1 PCa patients, and then it was validated using the TCGA-PRAD and GSE220095 datasets. Adding serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) values to the four-gene signature increased the performance to identify pN1 (HTP [AUC = .8487, p = 2.18e-09], TCGA-PRAD [AUC = .7150, p = 8.66e-08] and GSE220095 datasets [AUC = .8772, p = 4.09e-07]). Paired miR analyses showed that eight miRs were significantly upregulated in primary PCa that were pN1 (p < .01). The eight-miR signature performance increased when adding PSA (WTA dataset [AUC = .8626, p = 4.66e-10]) or Grade group (WTA dataset [AUC = .8689, p = 2e-10]). When combining the miR/mRNA signatures (miR-663b, CHRNA2 and PAH) with PSA levels, it showed the best performance to distinguish pN1 from pN0 PCa patients.
Conclusion: This study found miR/mRNA signatures in primary PCa tumours that in combination with serum PSA levels may complement nomograms for better detection of PCa patients with LNM and triage patients into better surgical decision-making.
Key points: Primary prostate cancer (PCa) tumours from patients pathologically diagnosed as N0 (pN0) or N1 (pN1) were dually assessed for microRNA (miRs) and mRNA levels using an NGS-based assay. A four-mRNA and an eight-miRNA signature were found. The mRNA signatures were further validated using two datasets. The combination of serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels or Grade Group with the miR/mRNA signatures separates pN1 from pN0 PCa patients.
Keywords: lymph node dissection; lymph node metastasis; mRNA‐signature; prostate cancer.
© 2025 The Author(s). Clinical and Translational Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Shanghai Institute of Clinical Bioinformatics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Urinary microRNA-based signature improves accuracy of detection of clinically relevant prostate cancer within the prostate-specific antigen grey zone.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Jun;13(6):4549-60. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5095. Epub 2016 Apr 8. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27081843 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA alteration and putative target genes in high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and prostate cancer: STAT3 and ZEB1 are upregulated during prostate carcinogenesis.Prostate. 2016 Jul;76(10):937-47. doi: 10.1002/pros.23183. Epub 2016 Mar 28. Prostate. 2016. PMID: 27017949
-
Identification of the Optimal Candidates for Nodal Staging with Extended Pelvic Lymph Node Dissection Among Prostate Cancer Patients Who Underwent Preoperative Prostate-specific Membrane Antigen Positron Emission Tomography. External Validation of the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center and Briganti Nomograms and Development of a Novel Tool.Eur Urol Oncol. 2023 Dec;6(6):543-552. doi: 10.1016/j.euo.2023.05.003. Epub 2023 Jun 1. Eur Urol Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37270378
-
Expression of miR-132 and miR-212 in prostate cancer and metastatic lymph node: Case report and revision of the literature.Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2020 Oct 1;92(3). doi: 10.4081/aiua.2020.3.209. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2020. PMID: 33016047 Review.
-
Management of Patients with Node-positive Prostate Cancer at Radical Prostatectomy and Pelvic Lymph Node Dissection: A Systematic Review.Eur Urol Oncol. 2020 Oct;3(5):565-581. doi: 10.1016/j.euo.2020.08.005. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Eur Urol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32933887
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
