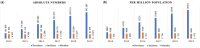Heart failure burden in Kazakhstan among adults: data from Unified National Electronic Healthcare System 2014-19
- PMID: 40219639
- PMCID: PMC12196695
- DOI: 10.1093/eurpub/ckaf049
Heart failure burden in Kazakhstan among adults: data from Unified National Electronic Healthcare System 2014-19
Abstract
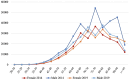
Heart failure (HF) is a complex clinical syndrome with significant mortality risks, causing an increasing healthcare burden. Globally, 64.3 million prevalent cases were estimated in 2017. This research examines HF epidemiology in the adult population in Kazakhstan, the largest country in Central Asia. The retrospective analysis was performed on data from the Unified National Electronic Health System, involving 526 766 individuals registered with HF between 2014 and 2019. In the cohort, women accounted for 54% and men for 46%, and the majority (87%) were aged 50 or above. The most prevalent comorbid conditions were hypertension (46%), cerebrovascular diseases (32%), and atherosclerotic heart disease (23%). While the incidence rate declined over the observation period, the all-cause mortality rate almost tripled from 356 to 975 people per million population during the observation period. Of the cohort, 14% of the patients (71 591) were recorded as deceased. In 2019, HF in Kazakhstan resulted in the loss of 2364789.8 disability-adjusted life years. Premature death accounted for a major portion, with 1337578.9 years of life lost. Males have a higher risk of death compared to females [hazard ratio (HR) = 1.24, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.23-1.26]. History of acute myocardial infarction increases the risk of death by 69% (HR = 1.69, 95% CI: 1.67-1.73) and diabetes by 14% (HR = 1.14, 95% CI: 1.12-1.16) after adjustment for other variables. This research evaluated the burden and disability-adjusted life years of HF in Kazakhstan. The results show that more effective disease management systems and preventive measures for the elderly are needed.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Public Health Association.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Surveillance for Violent Deaths - National Violent Death Reporting System, 50 States, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico, 2022.MMWR Surveill Summ. 2025 Jun 12;74(5):1-42. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss7405a1. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2025. PMID: 40493548 Free PMC article.
-
Burden of disease and treatment patterns in patients with vitiligo: findings from a national longitudinal retrospective study in the UK.Br J Dermatol. 2024 Jul 16;191(2):216-224. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae133. Br J Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38534198
-
Effects of a gluten-reduced or gluten-free diet for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 24;2(2):CD013556. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013556.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35199850 Free PMC article.
-
[Disease burden and clinical status of congenital heart disease combined with heart failure in China: a survey and analysis].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2025 Feb 2;63(2):148-156. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112140-20241031-00772. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 39844489 Chinese.
-
Beta-blockers in patients without heart failure after myocardial infarction.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Nov 5;11(11):CD012565. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012565.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34739733 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bozkurt B, Coats AJS, Tsutsui H et al. Universal definition and classification of heart failure: a report of the Heart Failure Society of America, Heart Failure Association of The European Society of Cardiology, Japanese Heart Failure Society and Writing Committee of The Universal Definition of Heart Failure. J Card Fail 2021;27:387–413.
-
- Savarese G, Becher PM, Lund LH et al. Global burden of heart failure: a comprehensive and updated review of epidemiology. Cardiovasc Res 2023;118:3272–87. - PubMed
-
- Bragazzi NL, Zhong W, Shu J et al. Burden of heart failure and underlying causes in 195 countries and territories from 1990 to 2017. Eur J Prev Cardiol 2021;28:1682–90. - PubMed
-
- Gusmanov A, Zhakhina G, Yerdessov S et al. Review of the research databases on population-based registries of unified electronic healthcare system of Kazakhstan (UNEHS): possibilities and limitations for epidemiological research and Real-World evidence. Int J Med Inf 2023;170:104950. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous