Oxygen extraction fraction changes in ischemic tissue from 24-72 hours to 12 months after successful reperfusion
- PMID: 40219845
- PMCID: PMC11993554
- DOI: 10.1177/0271678X251333940
Oxygen extraction fraction changes in ischemic tissue from 24-72 hours to 12 months after successful reperfusion
Abstract
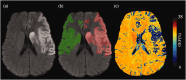
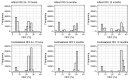
Oxygen Extraction Fraction (OEF) is a critical measure of a tissue's metabolic state post-ischemic stroke. This study investigated OEF changes in stroke-affected tissue compared to healthy tissue, post-reperfusion. OEF maps generated from gradient echo MRI images of 87 ischemic stroke patients at three time points after successful Endovascular Thrombectomy (EVT) were analysed in a prospective longitudinal multicentre study. Regions of interest (ROIs) delineating the infarct areas and corresponding mirror regions were drawn. The MR-derived OEF index values were obtained from the ROIs and compared using Wilcoxon signed rank tests. The cross-sectional comparison of OEF index values revealed lower values in the infarct areas than the corresponding contralateral areas at all three time points after successful EVT, presented as median (interquartile range) [24-72 hours: 20.84 (17.56-26.82)% vs 27.56 (23.22-31.87)%; 3 months: 27.37 (23.28-30.35)% vs 32.55 (28.00-35.81)%; 12 months: 24.38 (22.35-29.77)% vs 29.39 (25.86-34.04)%, p < 0.001 for all three time points]. Longitudinally, relative OEF index values increased gradually over time [24-72 hours: 0.81 (0.67-0.87); 3 months: 0.86 (0.79-0.95); 12 months: 0.88 (0.75-0.95)]. The findings revealed that following successful EVT, OEF in infarct tissue improves over time, indicating potential tissue recovery.Trial registration name and URL: Post-Reperfusion Pathophysiology in Acute Ischemic Stroke https://trialsearch.who.int/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=ACTRN12624000629538.
Keywords: Heterogeneity; infarct; ischemic stroke; oxygen extraction fraction; successful reperfusion; tissue changes; tissue recovery.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Oxygen Extraction Fraction Mapping on Admission Magnetic Resonance Imaging May Predict Recovery of Hyperacute Ischemic Brain Lesions After Successful Thrombectomy: A Retrospective Observational Study.Stroke. 2024 Nov;55(11):2685-2693. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.124.047311. Epub 2024 Oct 11. Stroke. 2024. PMID: 39391984
-
Early Infarct Growth Rate Correlation With Endovascular Thrombectomy Clinical Outcomes: Analysis From the SELECT Study.Stroke. 2021 Jan;52(1):57-69. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.030912. Epub 2020 Dec 7. Stroke. 2021. PMID: 33280550
-
Expanding the Treatable Imaging Profile in Patients With Large Ischemic Stroke: Subanalysis From a Randomized Clinical Trial.Stroke. 2024 Jul;55(7):1730-1738. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.124.046828. Epub 2024 May 28. Stroke. 2024. PMID: 38804134 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Endovascular Thrombectomy for Large Vessel Occlusion Stroke Beyond 24 Hours From Time Last Known Well: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.World Neurosurg. 2025 May;197:123943. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2025.123943. Epub 2025 Mar 27. World Neurosurg. 2025. PMID: 40157452
-
Endovascular Thrombectomy for Carotid Pseudo-Occlusion in the Setting of Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Comparative Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2024 Sep 9;45(9):1241-1245. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A8268. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2024. PMID: 38575320 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bandera E, Botteri M, Minelli C, et al. Cerebral blood flow threshold of ischemic penumbra and infarct core in acute ischemic. Stroke 2006; 37: 1334–1339. - PubMed
-
- Latchaw RE, Yonas H, Hunter GJ, et al. Guidelines and recommendations for perfusion imaging in cerebral ischemia. Stroke 2003; 34: 1084–1104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

