Poly-(ADP-ribose) serves as a scaffold for the methyltransferase METTL3/14 complex in the DNA damage response
- PMID: 40219966
- PMCID: PMC11992677
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaf244
Poly-(ADP-ribose) serves as a scaffold for the methyltransferase METTL3/14 complex in the DNA damage response
Abstract
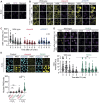
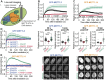
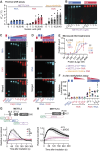
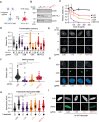
PARP1, a crucial DNA break sensor, synthesizes poly-(ADP-ribose) (PAR), a nucleic acid that promotes the recruitment of DNA repair proteins. Emerging evidence highlights a role of RNA and RNA-binding proteins in DNA repair. Notably, the RNA-m6A methyltransferase complex METTL3/14 is implicated in repairing ultraviolet-induced DNA lesions. Here, we dissected the interplay between the two nucleic acids PAR and RNA and how METTL3/14 recruitment and m6A accumulation at laser-induced DNA lesions responds to PAR dynamics. In vitro, METTL3/14 recognized both PAR and RNA, yet PAR presence did not inhibit the methyltransferase complex's catalytic activity. Acute knock-out of METTL3 rendered cells sensitive to transcription-blocking DNA damage and resulted in defects in transcription recovery and transcription-coupled DNA repair. Furthermore, combining METTL3 and PARP inhibitors led to an enhanced antiproliferative effect on cancer cells. Future therapeutic avenues may thus leverage the interplay between the nucleic acids PAR and RNA.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Conflict of interest statement
A.G.L. is a founder, CSO, and managing director of Eisbach Bio GmbH, a biotechnology company in oncology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CHD6 has poly(ADP-ribose)- and DNA-binding domains and regulates PARP1/2-trapping inhibitor sensitivity via abasic site repair.Nat Commun. 2025 Jan 25;16(1):1026. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-56085-5. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39863586 Free PMC article.
-
MORC2 regulates DNA damage response through a PARP1-dependent pathway.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Sep 19;47(16):8502-8520. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz545. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31616951 Free PMC article.
-
Differential and Concordant Roles for Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase 1 and Poly(ADP-Ribose) in Regulating WRN and RECQL5 Activities.Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Dec;35(23):3974-89. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00427-15. Epub 2015 Sep 21. Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26391948 Free PMC article.
-
Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase (PARP) and PARP Inhibitors: Mechanisms of Action and Role in Cardiovascular Disorders.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2018 Dec;18(6):493-506. doi: 10.1007/s12012-018-9462-2. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29968072 Review.
-
Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation by PARP1: reaction mechanism and regulatory proteins.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 May 7;47(8):3811-3827. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz120. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30799503 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

