Oxidative stress at telomeres triggers internal DNA loops, TRF1 dissociation, and TRF2-dependent R-loops
- PMID: 40219969
- PMCID: PMC11992676
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaf285
Oxidative stress at telomeres triggers internal DNA loops, TRF1 dissociation, and TRF2-dependent R-loops
Abstract
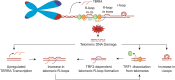
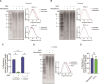
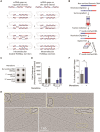
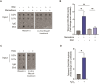
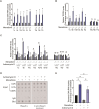
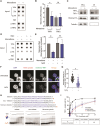
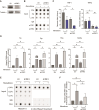
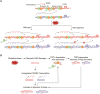
Telomeres are the nucleoprotein structures at chromosome ends. Telomeres are particularly sensitive to oxidative stress, which can induce telomere damage, shortening, and premature cellular senescence. How oxidative damage influences telomere structure has not been defined. Here, we induce oxidative damage at telomeres using menadione, which damages mitochondria mimicking intrinsic oxidative stress. We find that oxidative stress induces at telomeres single-stranded DNA breaks, internal DNA loop structures, dissociation of the shelterin component TRF1, upregulation of TERRA long noncoding RNA, and increased DNA:RNA hybrid structures known as R-loops. R-loop formation is enhanced not only in cis at telomeres, which show increased TERRA transcription, but also in trans at telomeres at which TERRA transcription is not induced indicating post-transcriptional R-loop formation. Finally, we show that oxidative damage induced R-loop formation requires TRF2, whose R-loop promoting activity may be unleashed upon TRF1 dissociation from telomeres. Altogether, our findings uncover in response to oxidative stress major remodelling of telomeric DNA, RNA, and shelterin complexes, and they unravel a physiological role of TRF2's ability to stimulate TERRA R-loop formation. We propose that the identified structural changes may facilitate DNA damage signalling and repair pathways to maintain telomere integrity during development and aging.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

