Enhanced Intracellular IR780 Delivery by Acidity-Triggered PEG-Detachable Hybrid Nanoparticles to Augment Photodynamic and Photothermal Combination Therapy for Melanoma Treatment
- PMID: 40219978
- PMCID: PMC12093379
- DOI: 10.1021/acsabm.5c00144
Enhanced Intracellular IR780 Delivery by Acidity-Triggered PEG-Detachable Hybrid Nanoparticles to Augment Photodynamic and Photothermal Combination Therapy for Melanoma Treatment
Abstract
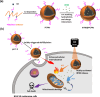
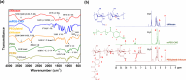
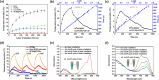
The PEGylation of drug-carrying nanoparticles has often been used to prolong blood circulation and improve drug deposition at tumor sites. Nevertheless, the PEG-rich hydrophilic surfaces retard the release of the payloads and internalization of therapeutic nanoparticles by cancer cells, thus lowering the anticancer efficacy. To boost the anticancer potency of the combined photodynamic therapy (PDT) and photothermal therapy (PTT) against melanoma by conquering the PEG dilemma, herein, the hybrid PEGylated chitosan-covered polydopamine (PDA) nanoparticles (PCPNs) with acidity-elicited PEG detachment ability were fabricated as carriers of IR780, a small-molecule photosensitizer used for PTT and PDT. The IR780@PCPNs displayed a uniform, solid-like spherical shape and sound colloidal stability. Under near-infrared (NIR) irradiation, the IR780@PCPNs showed prominent photothermal conversion efficiency (ca. 54.6%), robust photothermal stability, reduced IR780 photobleaching, sufficient singlet oxygen (1O2) production, and glutathione-depleting ability. Moreover, with the environmental pH being reduced from 7.4 to 5.0 at 37 °C, the decreased interactions between IR780 and PCPNs due to the increased protonation of phenolic hydroxyl residues within PDA and primary amine groups of chitosan accelerated the release of IR780 species from IR780@PCPNs. Importantly, the cellular uptake of IR780@PCPNs by B16F10 melanoma was remarkably promoted in a weakly acidic milieu upon PEG detachment driven by the disintegration of acid-labile benzoic imine. With NIR irradiation, the internalized IR780@PCPNs generated hyperthermia and 1O2 to damage mitochondria, thereby effectively inhibiting the proliferation of B16F10 cells. Collectively, our findings present a practical strategy for amplifying the anticancer efficacy of PTT combined with PDT using PEG-detachable IR780@PCPNs.
Keywords: IR780; PEG detachment; benzoic imine bond; melanoma treatment; photothermal and photodynamic therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Oxidative stress-augmented Cu-doped hollow mesoporous carbon nanozyme for photothermal/photodynamic synergistic therapy.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2025 Apr;683(Pt 1):910-925. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2024.12.076. Epub 2024 Dec 13. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2025. PMID: 39709766
-
PEGylated chitosan-coated nanophotosensitizers for effective cancer treatment by photothermal-photodynamic therapy combined with glutathione depletion.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 May;266(Pt 2):131359. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131359. Epub 2024 Apr 4. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38580018
-
Multifunctional Near Infrared Polymer Dots for Enhanced Synergistic Photodynamic/Photothermal Effect In Vitro.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2025 Feb 17;8(2):1278-1291. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.4c01593. Epub 2025 Jan 22. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2025. PMID: 39841131
-
Tumor-activated targetable photothermal chemotherapy using IR780/zoledronic acid-containing hybrid polymeric nanoassemblies with folate modification to treat aggressive breast cancer.Nanoscale. 2024 Jan 18;16(3):1415-1427. doi: 10.1039/d3nr05637f. Nanoscale. 2024. PMID: 38167914
-
Integrating Photothermal, Photodynamic, and Chemodynamic Therapies: The Innovative Design Based on Copper Sulfide Nanoparticles for Enhanced Tumor Therapy.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2025 Jan 20;8(1):676-687. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.4c01538. Epub 2024 Dec 30. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2025. PMID: 39829270
References
-
- Araújo J. L.; da Silva P. B.; Fonseca-Santos B.; Báo S. N.; Chorilli M.; de Souza P. E. N.; Muehlmann L. A.; Azevedo R. B. Photodynamic Therapy Directed to Melanoma Skin Cancer by Thermosensitive Hydrogel Containing Chlorophyll A. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2023, 16, 1659.10.3390/ph16121659. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
